In today’s digital age, mobile phones have become an inseparable part of our lives. From work to entertainment, we rely on them constantly. However, growing concerns suggest that prolonged exposure to mobile radiation may have unintended health consequences, particularly on fertility. But how much of this concern is backed by science, and what can we do about it? Let’s explore.
Mobile phones emit radiofrequency electromagnetic fields (RF-EMFs), a type of non-ionizing radiation. While these waves are not strong enough to directly damage DNA like ionizing radiation (e.g., X-rays), some research indicates that prolonged and close exposure to RF-EMFs may lead to biological changes, including oxidative stress, increased temperature, and possible DNA fragmentation—all of which could impact fertility.
1. Reduced Sperm Quality
Several studies suggest that men who keep their phones in their pockets for extended periods may experience:
Decreased sperm motility and viability 🏃♂️❌
Lower sperm concentration ⚖️
2. Increased Testicular Temperature
Keeping a phone close to the groin area, such as in trouser pockets, may cause a slight increase in testicular temperature. Since sperm production is temperature-sensitive, prolonged exposure could negatively affect sperm count and quality.
3. Oxidative Stress
RF-EMFs may lead to increased oxidative stress, resulting in cellular damage and inflammation in reproductive tissues, further impacting fertility potential.
While research on female fertility and mobile radiation is less extensive, there are growing concerns about:
1. Ovarian Reserve and Egg Quality
Some studies suggest that exposure to RF-EMFs could impact ovarian reserve (the number of healthy eggs available for fertilization) and overall egg quality, potentially affecting fertility outcomes.
2. Hormonal Imbalances
The endocrine system, which regulates reproductive hormones, may be sensitive to prolonged electromagnetic exposure, potentially leading to disruptions in menstrual cycles and ovulation.
3. Impact on Embryo Development
Research on animal models suggests that RF-EMFs may affect early embryonic development and implantation. However, human studies are still inconclusive.
While research is ongoing, it’s always best to take precautionary steps to minimize exposure and reduce potential risks:
✅ Keep Your Phone Away from Reproductive Organs – Avoid keeping your phone in your pocket or resting it on your lap for extended periods.
✅ Use Speakerphone or Wired Earphones – This minimizes direct exposure to radiation from mobile devices.
✅ Limit Screen Time Before Bed – Excessive phone usage before sleep can disrupt melatonin production, which plays a role in reproductive health.
✅ Switch to Airplane Mode When Possible – This reduces exposure to electromagnetic waves when you’re not using your phone.
✅ Avoid Sleeping Next to Your Phone – Place your phone at least a few feet away while sleeping to minimize prolonged exposure.
The impact of mobile telephony on fertility remains a subject of ongoing scientific research. While definitive conclusions are yet to be drawn, there is enough evidence to warrant precautionary measures. By adopting simple lifestyle changes, you can reduce unnecessary exposure and protect your reproductive health.
गर्भधारण में समस्या होने पर अधिकांश महिलाएँ चिंतित होती हैं, खासकर जब उनकी सभी स्वास्थ्य रिपोर्ट्स सामान्य होती हैं। इसके बावजूद गर्भधारण में दिक्कतें आ सकती हैं। इसके कई कारण हो सकते हैं, जिन्हें समझना महत्वपूर्ण है।
इसलिए, अगर सारी रिपोर्ट्स सामान्य हैं फिर भी गर्भधारण में समस्या हो रही है, तो इसका मतलब यह नहीं कि समस्या नहीं है। विशेष रूप से, व्यक्तिगत और व्यावसायिक सलाह लेना आवश्यक है ताकि सही निदान और उपचार प्राप्त किया जा सके।

















IVF means In-Vitro Fertilization, which is a type of assisted reproductive technology used to treat infertility. IVF is a procedure where the egg and sperm are placed together in a glass dish (in vitro) and then transferred into the womb.
IVF consists of several steps:
When it comes to starting a family, there are many different paths that couples can take. For some, conceiving naturally is the best and only option. However, for others, fertility treatments like in vitro fertilization (IVF) may be the best option for starting a family.
So, why should couples consider IVF? Here are four reasons:
IVF is an incredible medical breakthrough that has helped countless couples have children when they otherwise would not have been able to. Here are three benefits of IVF:
When it comes to in vitro fertilization (IVF), there are a lot of things to consider and a lot of things that can go wrong. That’s why it’s so important to be as prepared as possible and to know what to avoid during the IVF process.
One of the most important things to avoid during IVF is stress. Stress can have a negative impact on the success of IVF, so it’s important to find ways to relax and de-stress during the process.
There are a number of things that can help with this, including yoga, meditation, and spending time with friends and family.
Smoking and drinking can reduce your chances of getting pregnant during IVF. Alcohol can interfere with the success of IVF, and smoking can actually decrease the chances of IVF success.
If you’re trying to conceive, it’s best to avoid these things altogether.
It’s also important not to take certain medications during IVF.
Medications like anti-inflammatories and blood thinners can actually decrease the success of IVF, so it’s important to talk to your doctor about any medications you’re taking before starting the IVF process.
Finally, it’s important to avoid putting too much pressure on yourself during IVF. This process can be stressful enough without adding any additional pressure. Remember that the success of IVF depends on many factors, and even if everything goes perfectly, there’s no guarantee that you’ll conceive.
So, what should you avoid during IVF? Stress, alcohol, smoking, and certain medications are all things that can negatively impact the success of IVF. If you’re trying to conceive, it’s best to avoid these things and focus on relaxing and de-stressing as much as possible.
It is important to understand what are the limitations of IVF. Here are the three main limitations:
The hardest part about IVF is the emotional toll it takes.
The physical side of IVF is difficult, but it’s nothing compared to the emotional issues that arise during treatment. You might be surprised by how much you need to invest in yourself before and after your cycle.
Your mind is just as important as your body during treatment, so make sure you take care of yourself mentally as well as physically.
It can be tough to deal with all the feelings that come up when undergoing IVF treatment — sadness, anger, fear, and relief are just a few examples. And if you’re like most women who undergo fertility treatments, you’ll probably feel many different emotions more than once during this process.
Be diligent and constantly pay attention to your health. Always keep an eye on the symptoms that might appear during the IVF process, such as mood swings, fatigue, or headaches.
Take all the additional vitamins. There are a lot of unknowns when it comes to fertility hormones, but make sure you know what you should avoid during IVF treatment.
The success rate of IVF is a question many people have and it’s not a simple answer. There’s no one right answer to give, but many factors will come into play when determining the success rate of In-Vitro Fertilization.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a process of assisted reproductive technology (ART) in which eggs are retrieved from a woman’s ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a laboratory dish. The resulting embryos are then transferred to the woman’s uterus for implantation and pregnancy.
IVF can be an effective treatment for infertility, especially if you have any of the following conditions:
According to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM), the success rate of IVF depends on a number of factors, including the age of the patient, the cause of infertility, and the number of embryos transferred. The ASRM reports that patients under 35 with no fertility issues have about a 40% chance of success per cycle, while patients over 40 have about a 10-20% chance of success per cycle.
In vitro fertilization, or IVF, is a fertility treatment that involves retrieving eggs from a woman’s ovaries, fertilizing them with sperm in a laboratory dish, and then transferring the resulting embryos into the woman’s uterus.
IVF is often used as a last resort for couples who have been unable to conceive through other methods, such as artificial insemination or intrauterine insemination.
The success rate of IVF depends on many factors, including the age of the woman, the cause of infertility, the number of eggs retrieved, and the quality of the embryos.
In general, women under 35 have a higher chance of conceiving with IVF than women over 35. The live birth rate for women under 35 is about 40%, while the live birth rate for women over 35 is about 30%.
However, it’s important to remember that every couple’s situation is unique and that success rates can vary depending on the individual circumstances.
According to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM), about 60% of couples who use IVF will conceive.
There are many factors that affect a couple’s chance of conceiving with IVF. These include the woman’s age, the quality of her eggs, the health of her uterus, and the cause of infertility.
Some couples may have a higher chance of success with IVF than others. For example, younger women and those with healthy eggs have a better chance of conceiving with IVF. Couples who are infertile due to blocked fallopian tubes or sperm problems also have a higher success rate with IVF.
IVF is not right for everyone. Couples should talk to their doctor about their specific situation to see if IVF is right for them.
There are a number of potential side effects from IVF, some of which can be quite serious. These include ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), multiple births, and premature delivery. OHSS can cause pain, bloating, and nausea, and in severe cases can lead to kidney failure or blood clots. Multiple births are more likely with IVF than with natural conception, and can cause problems for both mother and child during pregnancy and delivery. Premature delivery is also a risk with IVF, as is low birth weight. Fortunately, most side effects from IVF are mild and temporary, and the vast majority of women who undergo the procedure go on to have healthy babies.
The success rate of IVF varies depending on a number of factors, but it is generally successful. However, this does not mean that IVF is the right choice for everyone. If you are considering IVF, be sure to speak with your doctor about all of the potential risks and benefits before making a decision.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a complex medical procedure used to help couples who are struggling to conceive. The process involves retrieving eggs from the woman, fertilizing them in a laboratory, and then transferring the embryos back into the woman’s uterus. While IVF can be expensive and time-consuming, it can also be a very effective way to help couples have the baby they’ve always wanted. If you and your partner are considering IVF, there are a few important tests that need to be done first. These tests will help your doctor determine if IVF is the right treatment for you.
If you’re considering in vitro fertilization (IVF), you may be wondering what tests are involved in the process. It’s important to remember that each person’s situation is unique, so your fertility specialist will tailor the testing to your specific needs. That said, there are some common tests that are often part of the IVF process.
There are a few different types of tests that are often involved in the IVF process. These tests help to ensure that everything is proceeding as it should and can help to identify any potential problems.
Some of the tests that may be involved in IVF include:
If you’re considering in vitro fertilization (IVF), you may be wondering what tests are involved in the process. Here’s a rundown of the tests that are typically done prior to starting IVF treatment.
Your first step will be to meet with a fertility specialist to discuss your medical history and whether IVF is right for you. If you decide to move forward with treatment, the next step will be to have some tests done.
One of the most important tests is an ovarian reserve test. This test measures the amount of eggs you have left in your ovaries. The results of this test will help your doctor determine how likely you are to respond to IVF treatment.
IVF is a big decision, and it’s important to be as prepared as possible before beginning the process. Here’s what you can expect during and after the testing process:
Before starting the IVF process, you’ll need to have a few tests done. These tests help to determine if you’re a good candidate for IVF and also help to assess your overall health. Your doctor will likely order blood tests, a vaginal ultrasound, and possibly a hysteroscopy.
The blood tests help to check your hormone levels and see how your ovaries are functioning. The vaginal ultrasound allows your doctor to get a better look at your uterus and fallopian tubes. And the hysteroscopy allows your doctor to take a closer look at your uterine lining.
After the testing is complete, your doctor will review the results with you and decide if IVF is the best course of treatment for you. If so, they’ll develop a treatment plan tailored specifically for you.
During the IVF process, you’ll be closely monitored by your doctor. You’ll likely have frequent blood tests and ultrasounds to check on your progress. You’ll also be given medication to help stimulate egg production.
The IVF process is a lengthy and expensive one, but it can be an extremely worthwhile investment for couples who are struggling to conceive. There are a number of tests that need to be done in order to determine whether or not IVF will be successful, and it is important to consult with a fertility specialist to see if this is the right option for you. With the help of modern medicine, many couples are able to have the children they always dreamed of.
In-vitro fertilization, or IVF, is a type of fertility treatment that involves fertilizing an egg outside of the body. Once the fertilized egg has been harvested, it’s then transferred to the woman’s uterus for implantation. Learn about all the stages of this process in this article!
IVF is a medical procedure in which eggs are retrieved from a woman’s ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a laboratory, before implantation.
The success rate for IVF depends on many factors, including the age of the woman, the cause of infertility, and the number of embryos transferred.
The first step in an IVF cycle is to trigger the ovaries through injectable hormones. This can result in multiple eggs which are then retrieved, fertilized, and implanted into the uterus. IVF can be an emotional roller coaster. It is important to have a support system in place during this process.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a fertility treatment in which egg cells are fertilized with sperm outside the body. This process is typically used when a woman’s fallopian tubes are blocked or when a man produces too few sperm.
The stages of in-vitro fertilization, or IVF, are multiple and complex. In order to understand how IVF works, it is first necessary to understand some basic reproductive biology.
IVF is a process by which eggs are removed from a woman’s ovaries and fertilized in a lab dish with sperm. The resulting embryos are then transferred back into the woman’s uterus, where they hopefully implant and grow into healthy babies.
The first stage of IVF is the ovarian stimulation phase, during which fertility drugs are used to help the ovaries produce multiple eggs.
Next is the egg retrieval phase, in which the eggs are harvested from the ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a lab.
After that, the embryo transfer phase takes place, in which one or more embryos are transferred to the uterus.
Finally, there is the waiting and praying phase, in which you wait to see if the embryos implant and pregnancy occurs.
IVF treatment is a complex medical procedure with a number of possible side effects. These can include:
If you are considering IVF treatment, it is important to be aware of the different stages involved. The process can be complex and time-consuming, but it can also be very rewarding. With the help of a qualified fertility specialist, you can increase your chances of success and give yourself the best possible chance of having a healthy baby.
There are many couples who are unable to conceive. It is unfortunate due to different reasons they are not able to conceive. That’s where technology helps them. IVF is one of the most advanced and effective methods that couples can use to become parents who were otherwise finding it difficult. If you are one of those who are looking for IVF you need to understand what IVF is and what are its pros and cons.
IVF- In Vitro Fertilization is a type of medication that is used to stimulate the development and release of women’s eggs. The egg and sperm are collected to fertilize in a laboratory. Then the embryo formed in the laboratory is placed into the woman’s uterus. Let’s find out some pros and cons of IVF:
Blockage in Fallopian Tubes: Many couples do not realize this until they face the problem of infertility. Often there are chances that the email fallopian tube is blocked which results in a pelvic infection that leads to infertility. When you are diagnosed with pelvic blockage, you can use IVF treatment to attempt pregnancy. During other pregnancy options like IUI Artificial insemination, it is important that the fallopian tube is open while with IVF, there is no such requirement
Lack of Ability to Fertilize the Egg: Generally, male fertility is the 40% cause of couples that need assistance in pregnancy. One of the major issues is the quality of sperm. In most cases, the quality of sperm fails to fertilize and creates infertility. With IVF the sperm and egg can close the proximity and fertilize the fertilization of egg for pregnancy.
Ovarian Failure: Young female premature ovarian failure or Peri-menopausal women that have low ovarian reserve can lead to infertility. In such a situation IVF can be a great option to conceive and achieve a successful pregnancy.
Same-sex Couple: Gone of the days when same-sex couples were used to consider taboo in society. Now slowly accepting same-sex couples. For such couples who wish to have a child, IVF can be a great opportunity to help them become parents. IVF Technology with sperm donors can help such couples with pregnancy.
Unsuccessful: Just like any other treatment, IVF is not a guaranteed treatment though the chances of failure are comparatively less. That doesn’t mean that the IVF cycle cannot be unsuccessful. The chances of its success depend on women and how your specialist proceeds.
Side Effects: IVF can be a great opportunity for couples to become parents. However, it comes with the chance of developing side effects. There is a small chance of developing Severe ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome but fortunately, the chances of this are small. During the process of IVF, there are many medicines that take place that can have side effects on your body.
Emotional and Psychological Toll: When you go through IVF treatment patients will find it emotionally and physically challenging. This can be a stressful experience for a partner as well as a family. So it is important for people to prioritize their psychological as well as emotional health during such procedures.
Expensive: IVF can provide hope for parents who are not able to conceive. However, one thing that can restrict them is the expense of IVF treatment. From medication to blood tests the cause can quickly burn a hole in your pocket.
Conclusion: IVF can be a great solution for many couples. However, you need to vary the pros and cons to ensure the best results. Keep
Infertility is a common problem, and there are many things that could cause it. However, not many people know about some of the more unusual reasons. If you’re thinking about IVF or trying to get pregnant in any way, there are a few things you should know to make your journey as easy as possible. In this blog, we’ll talk about some important things you need to know about IVF. We’ll also talk about some of the risks and problems that can happen.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a fertility treatment that uses sperm and eggs to be combined in a lab to create embryos. If the embryos are healthy, they can then be transferred to the uterus of a woman who is trying to conceive. IVF can be used by people of any age, but it is more commonly used by couples who are over 30 years old and have difficulty getting pregnant.
There are some risks that come with IVF. For instance, there is a chance of having an ectopic pregnancy, in which the embryo implants somewhere other than the uterus. An ectopic pregnancy can be very dangerous, and it may be needed to have surgery to get rid of it. After IVF treatment, there is also a chance of getting ovarian cancer. Most IVF pregnancies, though, end up with healthy babies.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a way for couples who can’t get pregnant naturally to get pregnant. There are many reasons why IVF is a good idea, such as:
Most likely, your first round of IVF will be the hardest. You may feel tired and uncomfortable initially, but these feelings usually go away after a few weeks. You will also need to take medicine to get your ovaries to work during your cycle. This can make you feel a little sick and give you painful abdominal cramps. After the first cycle, though, the process gets much easier.
Make sure you have a good fertility doctor. This is one of the most important things you can do to improve your IVF treatment. In addition, you can improve your experience with fertility treatment by doing a few things.
First, you should ensure that the IVF treatment you are getting is good. This means that your doctor is using the best methods and tools for medicine that are currently available. During your treatment, you should also make sure to eat a well-balanced diet. Eating healthy foods can make it easier for you to get pregnant. There is no one-size-fits-all way to make yourself more fertile, so be willing to try everything.
Trying to get pregnant can be scary, but with the right information and help, it can also be a very rewarding process. Before you try IVF or any other kind of fertility treatment, make sure you know all the risks and benefits. This blog has given you some important things to think about so that you can make the best decision you can before you jump in. Thanks for reading!
There are chances that your sperm count or sperm quality is poor which result in inability to conceive. In order to change your sperm quality and improve the chances of pregnancy, having a healthy diet can always be beneficial. There are different types of food items that you incorporate into your everyday meals to improve your health.
Fruits and Vegetables: Vegetables are one of the best foods to enhance semen quality. The antioxidants present in the fruits and vegetables like Cranberries or green can help you protect the sperm from cellular damage. It can help a speedy recovery. Moreover, the presence of Vitamin E and C can increase sperm count and movement. There are many green vegetables such as broccoli and Spanish, and fruits like mangoes and avocado that have Vitamin E. While Vitamin C can be found in oranges, tomatoes, and grapefruit. Vitamin B can be found in leafy game fruit beans with antioxidant properties. All these vitamins along with the antioxidant properties can keep the sperm free from chromosome abnormality.
Brazil Nuts: Excellent source of Selenium, Selenium for human health and is present for many processes including immune system functions, production of active thyroid hormone, helps motility. According to research, Selenium has an impact on infertile men. The treatment of Selenium by 50% of participants in a survey is able to increase this motility.
Tomatoes: Tomato is one of the best sources of vitamin C but also contains a plant nutrient lycopene. Lycopene is a nutrient that offers red color to fruits. It is one of the most powerful antioxidants that has many positive effects on male fertility. According to research, consuming 4 mg of lycopene every day can improve sperm count by 22 million/ml which is 25% of mortality.
Walnut: Walnuts are a great source of multiple nutrients including Omega 3, folate, B6, zinc, and antioxidants. The presence of two types of B vitamins – folate and B6 has a positive impact on male fertility and the quality of sperm. Folate is one of the most essential nutrients for male fertility that plays an important role in spermatogenesis.
Garlic: Many people do not know that garlic has so many nutrients and vitamins that can help to increase sperm count. Garlic as a whole can have a positive impact on male fertility. According to the number of minerals and vitamins found in garlic, the antioxidant properties can help testosterone levels and sperm production. Moreover, there are other aspects of male fertility that can be impacted by garlic.
Seeds: Many seeds such as Pumpkin contain the amount of zinc and Omega 3 fatty acids that can help improve the quality of sperm. You can also try Flaxseed, Chia seed, or sunflower seed that contains Vitamin E and many antioxidants to improve the movement and quantity.
Conclusion: These are some of the food items that can help you improve sperm count. Often, lack of sex and chances of pregnancy is affected by sperm count and quality. Incorporating these foods into your diet can help you improve.
Infertility is a major concern for many couples, and in some cases, the only solution may be to pursue IVF. Learn from this article what the process entails and why it’s beneficial for such couples.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a process of fertilization where an egg is combined with sperm outside the body, in contrast to natural fertilization which occurs inside the body.
The process of IVF can be divided into four main steps:
If you’re considering in vitro fertilization (IVF), it’s important to understand the process and what you can do to prepare for it. Here’s a step-by-step guide to IVF:
A FET, or frozen embryo transfer, is a type of in vitro fertilization (IVF) procedure in which embryos that were previously frozen are thawed and transferred to the uterus.
FETs are often used when a woman has undergone IVF but did not conceive as a result of the fresh embryo transfer. They may also be used if a woman has had previous IVF cycles but has not been successful in conceiving.
The FET process typically takes place over the course of two to three weeks. The first step is to thaw the frozen embryos. This is done by slowly warming them to room temperature over the course of an hour.
Once the embryos have been thawed, they are transferred to the uterus through a catheter. The transfer itself takes only a few minutes, and you will likely be able to go home shortly after the procedure is completed.
In most cases, you will be asked to take progesterone supplements for 10-12 days after the transfer. Progesterone helps prepare the lining of the uterus for implantation and maintains a pregnancy in its early stages.
We hope this article has given you a better understanding of the process of IVF and what to expect at each step. IVF can be a complex and emotional journey, but it can also be an incredibly rewarding one. If you are considering IVF, we encourage you to speak with your doctor to get more information and to make sure it is the right decision for you.
IVF is a type of assisted reproductive technology that can help couples get pregnant. This blog will talk about the precautions you need to take during IVF so that the procedure goes well and you stay healthy.
Getting ready is the first step in any IVF procedure. Before starting a process, it’s essential to make sure that you have all of the tools and materials you’ll need. This will offer you the most suitable possibility of success. This includes everything from birth control pills to devices that track ovulation.
During IVF, you may also need painkillers and drugs to stop the body from rejecting the embryo. Before you start taking any medications, you should talk to your doctor about them so that the proper doses can be given.
One of the most critical parts of IVF is choosing the sperm. Most of the time, the best sperm are selected based on their genes and their ability to fertilize an egg. During the process, it is also important to make sure that the sperm are handled and stored in the right way to avoid any health risks
When the eggs are taken out is one of the most important parts of IVF. Egg retrieval can be done in your doctor’s office or a clinic 34 to 36 hours after the last injection and before you ovulate. To help increase the chances of fertilization, treatment should start as soon as possible after the egg is taken.
For IVF to work, you need to eat well because it helps your body and hence facilitates the production of eggs. Eating a healthy, well-balanced diet with lots of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help increase fertility. Also, you should stay away from foods that are high in fat, drinks with a lot of sugar, alcohol, and processed foods. A healthy diet can also help cut down on inflammation and stress. All of these things can help with fertility in different ways.
If you’re thinking about IVF, you might be wondering how to get the most out of the process. Here are some things you can do to make sure your treatment works as well as possible:
Some changes may surprise you by how well they work out.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a process that can be both helpful and hard. Before you get IVF treatment, you should take a few steps to make sure that your pregnancy goes as well as it can. By following these tips, you can make it more likely that your baby will be healthy and reduce any risks that might be involved.
IVF is a relatively new way for women who can’t get pregnant on their own to do so with the help of technology. This blog answers 6 of the most common questions about IVF.
In vitro fertilization, or IVF, is a process in which a woman’s eggs are taken from her ovaries and then fertilized outside her body. The goal of IVF is to help a couple get pregnant by using biotechnology. In addition, IVF can help women who have trouble getting pregnant or have problems with their fertility. This can be because of age, vitality, or many other reasons – physical and psychological. IVF is an arduous process that requires both the patient and the doctor to have a lot of patience and work hard. But it is one of the most effective ways to get pregnant.
The principal risks of IVF treatments are the risk of losing the pregnancy and the risk of having a child with a birth defect. But there are also some possible benefits to think about. Some of these benefits are the ability to have a baby in your own womb, a higher chance of getting pregnant, and a lower risk of genetic disorders. Before making a decision, it’s important to think about all the pros and cons of IVF treatment.
IVF is a fertility treatment that couples can use if they can’t have a baby on their own. IVF is one of the most common ways to treat infertility, and anyone over the age of 21 can use it.
Most people who start IVF treatment get pregnant within six months. But sometimes, it takes longer than six months to get pregnant. This is because some couples can’t get pregnant no matter how many times they try. Talk to your doctor if you are thinking about having a child through IVF.
If you’ve tried IVF more than once and still can’t get pregnant, there are a few things you can do to improve your chances:
If you want to try to get pregnant, the first thing you should do is make sure that IVF is the right choice for you. IVF costs a lot of money and takes a lot of time, so you need to be sure it’s the right choice for you and your family. When making this choice, you should think about your budget, your history of getting pregnant, and your religious beliefs, among other things. Talk to your doctor or a fertility specialist if you’re not sure if IVF is right for you.
Through this blog, we tried to provide answers to some of the most frequently asked questions about IVF. Hopefully, this will help you feel more informed and empowered as you go through this life-changing experience.
At first, IUI is a newer and less popular way to get pregnant. But this method has been gaining in popularity because it leads to success rates similar to IVF (50%). Many people who are having trouble conceiving have tried IUI and had success with it. Learn more about this method and if it might be the right one for you!
IUI is a fertility treatment that involves inserting sperm into a woman’s uterus to help her get pregnant. It is often used in cases where the man has low quality sperm, or when there are other issues with the sperm. IUI can also be done with drugs to increase chances of conception.
The success rate of IUI varies depending on the underlying cause of infertility, but it is generally considered to be a less invasive and less expensive option than in vitro fertilization (IVF). IUI is typically performed using a thin, flexible catheter that is inserted through the cervix into the uterus. The sperm is then injected into the uterus, where it hopefully will fertilize an egg and lead to pregnancy.
IUI can be an effective treatment for infertility, but it’s important to consult with a fertility specialist to determine if it’s the right treatment for you.
There are many reasons why people opt for intrauterine insemination (IUI) as a means of becoming pregnant. Some may have difficulty conceiving due to medical issues such as endometriosis or polycystic ovarian syndrome, while others may have male factor infertility. In some cases, IUI may be used in conjunction with fertility drugs in order to increase the chances of conception.
IUI is a treatment that can be used to help couples who are struggling to conceive. IUI involves placing sperm inside the woman’s uterus, which gives the sperm a better chance of fertilizing the egg. IUI can be used for couples who have unexplained infertility, mild endometriosis, or mild male factor infertility. IUI is also often used as a first-line treatment for couples who have been trying to conceive for less than a year.
If you and your partner have been trying to conceive without success, you may be considering intrauterine insemination (IUI).
The first step in preparing for an IUI cycle is to consult with a fertility specialist. They will perform tests to determine the cause of your infertility and whether IUI is likely to be successful for you.
Once it has been determined that IUI is a good option for you, you will need to take medication to stimulate your ovaries to produce multiple eggs. These medications are typically injected daily for about two weeks.
Around the time that your eggs are mature, you will have another ultrasound and blood test to determine when ovulation will occur. Once ovulation has been confirmed, the IUI procedure will be scheduled.
On the day of the procedure, your partner will need to provide a semen sample which will be used to prepare the sperm for insertion. You will then be asked to lie down on an exam table and insert a speculum into your vagina. A catheter will then be passed through the cervix into the uterus and the sperm will be injected.
If you are considering IUI as a way to get pregnant, it is important to understand the best time to do an IUI cycle. The optimum time for IUI is during the follicular phase of your menstrual cycle, when the eggs are mature and ready to be fertilized. This usually occurs around days 12-16 of your cycle.
Your doctor will likely recommend that you have an ultrasound on day 10 or 11 of your cycle to confirm that the eggs are maturing properly. Then, on the day of your IUI procedure, you will be given medication to stimulate ovulation. The timing of the IUI is very important; it must be done within 12 hours of when the ovulation medication is given.
If you are having trouble getting pregnant, you may want to consider IUI as a possible option. IUI is a new way to get pregnant that is less invasive and more affordable than other methods, such as IVF. IUI can be done at home or in a clinic, and it has a high success rate.
IVF is the most popular fertility treatment in India. IVF or In Vitro Fertilization involves taking sperm and eggs from the man and woman respectively and then combining them in a laboratory dish to allow fertilization to occur. The fertilized egg is then implanted back into the female partner’s uterus.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a fertility treatment in which eggs are retrieved from a woman’s ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a laboratory. The resulting embryos are then transferred to the woman’s uterus, where they hopefully implant and result in pregnancy.
IVF can be an option for couples who have been trying to conceive without success, as well as for women with certain medical conditions that make it difficult to get pregnant or carry a pregnancy to term.
There are many things to avoid during the process of in vitro fertilization or IVF. These include:
Additionally, it is important to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and to avoid stress as much as possible.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a fertility treatment in which eggs are retrieved from the ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a laboratory. The resulting embryos are then transferred to the uterus with the hope of achieving a pregnancy.
IVF is a complex and costly procedure, and it’s not always successful. In fact, according to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM), only about 40 percent of IVF cycles result in a live birth.
But for couples who have been struggling to conceive, IVF may offer their best or only chance of having a baby. Here’s a look at how the IVF process works.
According to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM), the success rates of in vitro fertilization (IVF) vary based on a number of factors. These factors can include the age of the woman, the cause of infertility, and the number of embryos transferred.
The ASRM reports that, in general, women under the age of 35 have a 40-50% chance of achieving a successful pregnancy with IVF. For women aged 35-37, the success rate is about 32-39%. Women aged 38-40 have a 23-27% chance of success, and those over 40 have a 12-20% chance.
The cause of infertility can also affect the success rate of IVF. For example, if the woman has blocked fallopian tubes, her success rate will be lower than if she has unexplained infertility. Similarly, if the man has a low sperm count, the success rate will be lower than if there were no obvious fertility issues.
There’s no specific age limit to go for IVF, but as you get older, your chances of success diminish. If you’re under 35, you have about a 40% chance of success with IVF, but if you’re over 40, that drops to about a 10% chance. So, while there’s no hard and fast rule, the general advice is to try IVF sooner rather than later if you’re hoping to conceive.
No, there is no specific age limit to go for IVF. However, it is important to note that fertility declines with age. This means that women over the age of 35 may have a more difficult time conceiving using IVF. Additionally, the success rates for IVF are lower for women over the age of 40.
So, there you have it—an overview of the IVF process from start to finish. Although it may seem like a daunting and complicated process at first, with the help of a fertility specialist and some financial planning, IVF can be an option for growing your family. And remember, you are not alone—over 5 million babies have been born worldwide through IVF.

Infertility treatments like in-vitro fertilization (IVF) have come a long way in recent years, but they’re still not foolproof. If you’re considering IVF, you’re probably wondering how many rounds it will take to get pregnant.
There’s no easy answer to that question because every couple is different and every IVF cycle is different. However, we can give you some general guidelines based on what’s typical.
In general, most couples will need to undergo 3-4 IVF cycles before they get pregnant. However, there are some couples who will get pregnant after just one cycle, while others may need to do 6 or more cycles.
The number of cycles you’ll need to undergo will depend on a number of factors, including your age, the cause of your infertility, and your response to the IVF medication.
If you’re younger than 35 and have no known fertility problems, you’re more likely to get pregnant after just one or two IVF cycles. However, if you’re older than 35 or have a known fertility problem, you may need to do more cycles.
The success rate for IVF also varies from cycle to cycle. In general, you have about a 30% chance of getting pregnant after each IVF cycle. So, if you do three cycles, your chances of getting pregnant are about 90%.
Of course, these are just averages and your actual success rate may be higher or lower. The only way to know for sure is to talk to your doctor and go through the IVF process.
If you’re considering IVF, remember that it’s a long and expensive process. It’s important to do your research and talk to your doctor to make sure it’s the right choice for you.
There is no upper limit to the age of women who can have IVF treatment.
However, the chances of success are lower in women over the age of 40.
The reason for this is that older women tend to have fewer eggs and these eggs may be chromosomally abnormal.
This means that there may not be enough healthy eggs to produce a baby, or there may be too many chromosomes in the egg.
The risk of miscarriage is also higher in older women.
There is no one answer to this question, as it can vary depending on a number of factors, including the couple’s fertility, the woman’s age, and the underlying reason for fertility treatment.
Generally speaking, most couples will undergo one or two cycles of IVF per year. However, some couples may undergo more, depending on their individual circumstances.
Age is one factor that can influence how many times a couple can do IVF in a year. For example, younger women may be able to tolerate more frequent cycles of IVF, while older women may need to space out their treatment more.
The underlying reason for fertility treatment can also play a role. Couples who are trying to conceive with IVF due to male factor infertility may need to do more cycles of IVF in a year, as sperm quality can decline over time.
Ultimately, the decision of how many times to do IVF in a year is one that should be made by the couple in consultation with their fertility doctor. They will take into account the couple’s individual circumstances and make a recommendation based on what is best for them.
Two rounds of IVF are a good start for many couples.
Each round involves a great number of medical procedures, and the risks and side effects can be minor or major, depending on the couple.
However, even after two IVF treatments, these numbers are actually much more promising than they seem.
Millions of people have overcome infertility, and a relatively large number have done it without any difficulty at all. They may have had just one treatment or no treatments at all; often it was simply that they started trying for a baby sooner rather than later.
The process of in vitro fertilization (IVF) can be a long and daunting one for couples struggling with fertility issues. But with modern technology and advances in reproductive medicine, the IVF process has become much shorter and more successful than it was in the past. In this article, we’ll take a look at the average length of time it takes to complete the IVF process from start to finish.
IVF stands for in vitro fertilization. It is a type of assisted reproductive technology (ART) that involves retrieving eggs from a woman’s ovaries and fertilizing them with sperm in a laboratory dish.
IVF can be an option for couples who have been trying to conceive without success for some time. It may also be an option for women with damaged Fallopian tubes or men with low sperm counts.
The IVF process usually takes place over the course of several weeks and involves multiple steps.
This is done using medication that contains hormones, such as follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) or human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG). The medication is usually given through injections.
Once the eggs have reached a certain size, they are ready to be retrieved. A needle is inserted into the vagina, and the eggs.
The process of IVF can be a long and difficult one, but it is often worth it for couples who are struggling to conceive. The first step is to consult with a fertility specialist to see if IVF is right for you. If it is, the next step is to begin the process of stimulations and retrievals. This can take several weeks, during which time you will be closely monitored by your doctor. Once the eggs have been retrieved, they will be fertilized in a lab and then transferred back into your uterus. The entire process can take several months, but the results are often worth it for couples who have been struggling to conceive.
The success rates of IVF can vary depending on a number of factors, including the age of the patient, the cause of infertility, and the number of embryos transferred. In general, however, the success rate of IVF is about 20-35%.
The process can be long and complicated, and there are several risks and potential complications associated with it. Couples should discuss all of the risks and potential complications with their doctor before proceeding with IVF. Some of the risks and potential complications associated with IVF include:
This concludes our article on the timeline of IVF from start to finish. We hope that this has given you a better understanding of how long the entire process takes and what you can expect at each stage. If you have any further questions, please don’t hesitate to reach out to us or your fertility specialist.
Intrauterine insemination, or IUI, is a fertility treatment in which sperm is placed inside a woman’s uterus to facilitate fertilization.
The procedure is used when a man has a low sperm count or when the quality of his sperm is poor. IUI can also be used when a couple is experiencing unexplained infertility.
During IUI, a surgeon inserts a catheter into the woman’s uterus. The catheter is connected to a syringe that contains the man’s sperm. The sperm is then injected into the woman’s uterus.
IUI is usually performed using sperm that has been collected via ejaculation. However, in some cases, sperm may be retrieved directly from the testicles. This is known as testicular sperm extraction (TESE).
IUI is typically performed using gonadotropins, which are hormones that stimulate the ovaries to produce eggs. The woman is monitored closely during the treatment cycle to ensure that the eggs are released at the optimal time.
Once the eggs are released, they are fertilized with the man’s sperm in a laboratory. The fertilized eggs are then placed back into the woman’s uterus.
IUI is a relatively simple and low-risk fertility treatment. The success rate of IUI varies depending on the underlying cause of infertility. For example, IUI is more likely to be successful if the man has a low sperm count.
IUI is generally well tolerated by most women. The most common side effects are mild cramping and bloating.
IUI is a safe and effective fertility treatment for couples who are struggling to conceive. If you are considering IUI, be sure to speak with your doctor about your specific situation
Yes. A low sperm count can be the result of many things, including infections, injuries, and certain medications. For many men, the condition is temporary and will return to normal after a few months.
If your sperm count is low, several options are available for couples trying to conceive:
In vitro fertilization (IVF). In this procedure, eggs are removed from your ovaries and fertilized in a laboratory with sperm collected from you or your partner. The resulting embryo is then transferred into your uterus to allow implantation.
Intrauterine insemination (IUI). During IUI, washed sperm are placed directly into your uterus through a narrow plastic tube inserted into it. This procedure has been shown to be successful in treating male infertility when combined with other fertility treatments such as Clomid or gonadotropins.
The answer to this question is not straightforward. The number of motile sperm required for IUI depends on a number of factors, including the age of the woman, the duration of infertility, and whether or not she is having her first child.
In general, if you’re younger than 35 years old and have been trying to conceive for less than 6 months, your doctor may recommend that you undergo IUI with only 10 million motile sperm per cycle.
However, if you’re over 35 years old or have been trying for more than six months, your doctor may recommend that you undergo IUI with 20 million motile sperm per cycle.
The best age to do IUI is very much dependent on your own circumstances. If you are a woman who has had a problem with fertility, then the sooner you can get treatment the better.
For example, if a woman has had blocked fallopian tubes or endometriosis and has not conceived after 6 months of trying, then she may benefit from IUI treatment.
If a woman is aged over 35 years, then she is considered to be ‘older’ and it becomes increasingly difficult to conceive naturally as time goes by.
However, there are many women who have conceived naturally at this age because they have been trying for long enough and their partner’s sperm count is normal. This may sound strange but it does happen!
If you are 35 years old or over and have not conceived within 2 years of regular unprotected intercourse (without the use of any fertility drugs), then it is advisable to seek medical advice regarding your chances of conceiving naturally (or through other treatments) before turning to IVF treatment.
You are probably wondering how you can make your IVF treatment successful given that many people are not. However, if you prepare for your IVF and follow these tips you will be able to increase your odds of success.
Patients undergoing fertility treatment can utilize in vitro fertilization (IVF) to retrieve eggs. The eggs are then fertilized with sperm, and the patient is hopeful to develop an embryo.
IVF can be an effective fertility treatment for a variety of conditions that cause infertility. It is often used when other fertility treatments, such as medication or surgery, have not been successful.
There are several steps involved in the IVF process, and each step must be carefully monitored and controlled to ensure success.
Stimulating the ovaries. This is done with injectable medications that contain either follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) or human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Next, the eggs are retrieved from the ovaries using a needle that is inserted into the vagina under ultrasound guidance. The egg retrieval process takes about 30 minutes and is usually performed under sedation.
Once the eggs have been retrieved, they are placed in a dish with sperm for fertilization. The sperm may be obtained from the male partner through masturbation or may be donated by a sperm bank. In some cases, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) may be used, which involves injecting a single sperm directly into each egg.
After fertilization has occurred, the embryos are incubated in a laboratory for 3-5 days. During this time, they will divide and grow into larger cells.
Once they have reached the blastocyst stage, they are ready to be transferred to the uterus. The transfer is a simple procedure that is similar to a pap smear and is usually performed under ultrasound guidance.
After the embryos have been transferred, the patient will take medication to support the pregnancy. A pregnancy test is typically performed two weeks after the transfer.
If the test is positive, an ultrasound will be performed to confirm the pregnancy and to check for the presence of multiple gestations.
There are some basic tips that can help increase the chances of success with IVF. First and foremost, it is important to have a healthy lifestyle prior to starting an IVF cycle. This means eating a nutritious diet, getting regular exercise, and managing stress levels. Additionally, it is important to work closely with a fertility specialist to ensure that all steps of the IVF process are being followed correctly. Lastly, remaining positive throughout the process can also play a role in increasing the chances of success.
If you’re considering in vitro fertilization (IVF), there are a few things you can do to improve your chances of success. First, get as healthy as possible. Second, talk to your doctor about your medical history and what medications you’re taking. Some medications can improve your chances of success with IVF. Third, consider using an egg donor or sperm donor if you have trouble conceiving on your own. And finally, be prepared for the emotional roller coaster that is IVF. It’s normal to feel scared, anxious, and even overwhelmed at times. But remember, you’re not alone—thousands of couples go through IVF every year, and many of them are successful.
There is no single answer to the question of how to make your first IVF treatment successful. Every patient and every situation is unique. Stay positive and have faith that you will ultimately achieve your goal of becoming a parent. With these tips in mind, you can give yourself the best chance possible for a successful IVF treatment.
There’s a lot of misconceptions out there about what semen actually is and what it does. This article breaks down the truth behind semen, answering all your questions and clearing up misconceptions.
The average volume of semen produced by a man is about 3.4 ml. Sperm are the cells that fertilize a female’s egg during sexual intercourse, resulting in pregnancy. Semen is produced in the testicles and stored in the epididymis.
The average volume of semen produced per ejaculation is between 2 and 5 milliliters. The average concentration of sperm in an ejaculation is between 40 and 300 million sperm per milliliter. Sperm makes up only about 1% of semen by volume.
If you’re producing semen, chances are good that you’re doing it right. But how much semen should you produce? The answer may surprise you.
According to a study published in the journal Andrology, the average man produces about 3.4 mL of semen per ejaculation. That’s about one teaspoonful. However, your mileage may vary. Some men produce more semen than others. And some men produce less.
So what’s the big deal? Well, for one thing, semen is full of nutrients that are essential for your health. It’s also a source of pleasure for many men (and their partners). So if you’re not producing enough semen, you may be missing out on some of the benefits of ejaculation.
Fortunately, there are things you can do to increase your semen production. If you’re concerned about your output, talk to your doctor or a sex therapist. They can help you figure out if there’s a problem and what steps you can take to improve things.
Sperm is released during ejaculation and is responsible for fertilizing an egg. Sperm can live inside a woman’s body for up to five days, which means that pregnancy is possible even if intercourse occurs several days before ovulation.
How long semen remains viable depends on a number of factors, including the health of the sperm and the conditions in which it is stored. Sperm can live for up to five days in a woman’s reproductive tract, but they are more likely to live for two to three days. The viability of sperm decreases after ejaculation, so it is best to have intercourse as close to ovulation as possible.
Sperm can travel up the vagina and into the fallopian tubes, where an egg is usually waiting. If the sperm fertilizes the egg, this causes pregnancy.
However, for pregnancy to happen, a lot of things need to be just right. The sperm has to be healthy and strong, and the egg has to be in just the right place at just the right time. This means that even if you have sex when you’re ovulating (when your egg is ready to be fertilised), you still might not get pregnant. There are lots of myths about how you can or can’t get pregnant from different sexual activities.
Semen is the fluid that is released from the penis during ejaculation. While semen itself does not cause sexually transmitted infections (STIs), it can transmit them. This is because STIs can be present in the semen of an infected person. When someone with an STI ejaculates, their infected semen can enter the body of their sexual partner, causing them to become infected.
There are a few ways to reduce the risk of transmitting STIs through semen. One is to use a condom during sex. Condoms create a barrier between the penis and the body of the sexual partner, which can prevent semen from entering the body.
Another way to reduce the risk of transmitting STIs through semen is to have your partner get tested for STIs before having sex.
Now that you know everything there is to know about semen, don’t be afraid to ask questions and learn more about this fascinating subject. After all, knowledge is power! Understanding how your body works can only lead to good things, so get out there and start learning. Who knows, you might just find that you have a new appreciation for this amazing bodily fluid.
As you watch your belly grow bigger and feel your baby move inside of you, it’s hard to believe that just a few short months ago, your baby was just a single cell. But that’s the amazing thing about embryology: the science of how a baby develops from that single cell into a fully formed human being, ready to enter the world.
If you’re curious about how your baby went from zygote to fetus to newborn, read on to learn more about the fascinating science of embryology.
Embryology is the study of the development of an embryo from the fertilization of the ovum until birth. It covers a vast array of topics, including genetics, cell biology, anatomy, and physiology.
Embryology is a critical science that helps us understand how an organism develops from a single cell into a complex being. This knowledge is essential for medical and scientific advancements, as it allows us to better understand and treat birth defects, genetic disorders, and other developmental problems.
The field of embryology has come a long way since its humble beginnings in the early 1800s. In the early days of embryology, scientists were limited to studying embryos that had already been born.
Now, thanks to advances in technology, we can study embryos in the womb, giving us a much more intimate look at development.
Embryology is divided into two main branches:
Developmental embryology is further divided into two sub-branches:
Evolutionary embryology, on the other hand, is concerned with how embryos have changed over time in response to their environment.
Embryology is an important science with far-reaching implications. It helps us understand the complexities of human development and can be used to improve our health and the health of future generations.
The journey to becoming a baby starts with conception when the sperm fertilizes the egg. This single cell, now called a zygote, contains all of the genetic information that will determine your baby’s sex, hair and eye color, and much more.
The zygote begins to divide into two cells, then four, then eight, as it makes its way through the fallopian tube to the uterus. Once the zygote reaches the uterus, it implants in the lining of the uterus and begins to grow.
During the first trimester of pregnancy, your baby grows and develops rapidly. The heart and brain begin to form, and by the end of the first trimester, your baby’s heart is beating and he or she has developed all of the organs and systems that will be present at birth.
During the second and third trimesters, your baby continues to grow and develop. The bones and muscles begin to grow and strengthen, and by the end of the third trimester, your baby is fully formed and roughly the size of a watermelon.
The final weeks of pregnancy are spent in the womb, where your baby continues to grow and develop, gaining weight and getting ready for life outside the womb.
When your baby is ready to be born, labor and delivery begin. The muscles of the uterus contract and the baby is pushed through the birth canal. After a few hours (or sometimes days) of labor, your baby is born!
Welcome to the world, little one!
When you think about trying to conceive, your age is probably one of the first things that come to mind. And it’s true that age is a major factor in fertility. But it’s not the only factor. Your age, combined with the age of your eggs, as well as your general health, all play a role in your fertility.
Your age is the most important factor in your fertility. As you age, your eggs age with you.
In your early to mid-20s, you have about a 20% chance of getting pregnant each month.
By age 30, your chance of getting pregnant each month starts to decline.
Your chance of becoming pregnant each month by the age of 35 is only slightly higher than it was in your twenties.
Furthermore, your chance of becoming pregnant each month by the age of 40 is only about 5%.
In addition to your age, the quality of your eggs also plays a role in your fertility. As you age, the quality of your eggs declines. This is why your chance of getting pregnant declines as you age.
The quality of your eggs is measured by something called the anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH). AMH is a hormone produced by the cells that surround your eggs. The higher your AMH level, the higher the quality of your eggs.
Your general health also plays a role in your fertility. Conditions like obesity, diabetes, and high blood pressure can all impact your fertility.
There are things you can do to improve your fertility, no matter your age. If you’re a smoker, quitting smoking can improve your fertility. If you’re overweight, losing weight can also improve your fertility.
And if you have a medical condition that’s impacting your fertility, there may be treatments that can help. For example, if you have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a common cause of infertility, there are treatments that can help you get pregnant.
If you’re having trouble getting pregnant, talk to your doctor. They can help you figure out what might be causing your fertility problems and what you can do about it.
Yes, you can improve your AMH levels. But unfortunately, it’s not as easy as popping a few supplements or taking some drugs.
The good news is that there are several things you can do to naturally boost your AMH levels, including:
VAC has been shown to increase AMH levels by up to 88% in clinical studies, and it’s been used for hundreds of years to enhance fertility in both men and women.
VAC works by helping the pituitary gland produce more luteinizing hormone (LH), which is then released into the bloodstream and travels onto the testicles where it signals them to produce testosterone.
There are many factors that play a role in whether or not you’ll get pregnant, and AMH is just one of them. But before you try to conceive, it’s important to work with your doctor to find the right treatment plan for you based on all of your individual factors and preferences.
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a procedure that combines egg and sperm in a lab dish to create an embryo, which is then transferred to the uterus.
The process involves stimulating your ovaries with fertility drugs and/or hormone injections and monitoring the growth of follicles (eggs) in your ovaries. Also, retrieving them through transvaginal ultrasound-guided aspiration, or surgical removal.
The eggs are then fertilized with sperm in a petri dish and the resulting embryos are monitored until they reach the desired stage of development. One or more healthy embryos are then transferred into your uterus via a catheter (a thin tube).
IVF is often used when other treatments, such as intrauterine insemination (IUI), have been unsuccessful at achieving pregnancy. IVF also may be used if you have blocked fallopian tubes, certain male infertility problems, or for other reasons.
If you’ve been trying to conceive without success, you may be considering in vitro fertilization (IVF). IVF is an assisted reproductive technology (ART) that can help you achieve pregnancy.
While IVF may seem like a daunting and expensive option, it is actually one of the most effective fertility treatments available. Here are five reasons why IVF may be the best option for you:
The success rate of IVF depends on a number of factors, including the age of the woman and the quality of the eggs. However, overall, IVF has a high success rate.
According to the American Society for Reproductive Medicine (ASRM), the success rate of IVF is about 40 percent for women under 35. The success rate declines as a woman’s age increases.
One of the great things about IVF is that it can help you conceive twins or triplets. In fact, about 30 percent of IVF pregnancies result in twins.
While having twins or triplets may not be what you originally planned, it can be a great blessing.
If you have male factor infertility, IVF can help. Male factor infertility is a condition in which the man’s sperm is unable to fertilize the woman’s egg.
In IVF, the man’s sperm is injected directly into the woman’s egg. This bypasses the need for sperm to travel through the man’s reproductive tract.
For women with female factor infertility, IVF can help them become pregnant.
Female factor infertility is a condition in which the woman’s reproductive system is unable to support a pregnancy.
There are many causes of female factor infertility, including endometriosis, uterine fibroids, and polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). IVF can help you conceive even if you have one of these conditions.
IVF helps many women, including those with fertility problems like you, become pregnant.
Fertility problems can be caused by a variety of factors, including age, lifestyle, and health conditions.
IVF can help you overcome these obstacles and give you the best chance of conceiving.
If you’ve been trying to conceive without success, IVF may be the best option for you. IVF is a highly effective fertility treatment that can help you overcome a variety of fertility problems.
IVF fertility treatments are the fastest way for a couple who has been having trouble getting pregnant, to finally achieve their dream of starting a family.
It is not uncommon for couples to feel frustrated that they have not been able to conceive naturally after several months. Many end up giving up and resigning themselves to being childless.
However, there is hope as most often than not, this infertility is due to an underlying condition or factor that can be resolved with early detection using techniques like IVF.
Reasons for IVF Failure – With the advancement in technology and better care facilities, the success rate for IVF is at its highest. In spite of this, there are cases where IVF fails. All this results in deep pain for the couple who wishes to parent a child. A couple who choose IVF for the treatment of their infertility spend a lot of money, and years of their life devoted, and in the last nothing is achieved. In this situation they might feel cheated, scammed, and slighted. In this case, the couple has two areas for consideration at this point: the emotional response to the loss that needs to be processed and the medical choices that need to be made regarding the next steps in the fertility journey. Many women who have had a failed IVF cycle will be successful on a second or even a third cycle. Not all the issues that influence IVF success can be corrected, but some can be addressed to help make the next cycle more likely to result in pregnancy including:
For the success of IVF, the age of the female partner is very important. As the age of women advances, their eggs also get older. As the age advances, fewer eggs are produced and the quality of the eggs decreases. All this begins to happen when the women are in their thirties, and the decline accelerates when the age reaches 37. The chance that an IVF cycle using fresh non-donor eggs will result in a live birth is, on average, almost 32 percent for a 35-year-old woman, but only 12 percent for a 41 or 42-year-old woman.
Poor embryo quality is another reason for the failure of the IVF cycle. Due to genetics or chromosomal disorders, the embryos generally fail to implant and grow. Again, older eggs are more likely to result in poor embryo quality.
The ovaries respond to the fertility medications with the production of multiple eggs, which is critical to the chances of conceiving with IVF. In some cases, women do not produce multiple eggs because their ovaries have fewer numbers of eggs in reserve than expected.3
Take a break after this loss. It is important because it helps to cope with the loss. The whole process of the IVF cycle takes a long time and gives a huge emotional and physical toll on your body. Take a week off from everything so that you can take care of and nurture yourself. Use this time to eat your favorite food or listen to your favorite music or engage yourself in sports or activities which like most. It is also recommended to take emotional support from a good licensed counselor.
After expressing a long deep emotional pain, it is necessary to pick yourself up and plan a meeting with your fertility specialist or doctor. The fertility specialist will review all the details of your cycle begins with the results of your ovarian stimulation, any egg quality or quantity issues, and any embryo development or transfer issues.
Meeting with your fertility specialist gives you a chance to discuss any new type of information learned from the cycle to then proceed with a more informed treatment plan for the next cycle. However, the emotional impact is very much, the failed cycle may provide some important information to the physician about you, your embryos, and what might be changed for the future to help increase your chances of success.
After the first round of a failed IVF cycle, patients may blame themselves for the loss or the failure. The number one step in preparing emotionally for the second round of the IVF process is accepting that it’s not your fault. There is not always a scientific reason as to why your IVF cycle failed. Sometimes, these procedures are successful, and sometimes, they are not.
Keep in mind that you have gone through the IVF process once already. The most challenging part is letting go of your expectations because they may affect you emotionally. Once you begin the second round of IVF following a failed cycle, it is a good idea to remind yourself to stop asking so many questions about your follicle counts or egg quality.
After an IVF process failure, your doctor will let you know in detail what they’ve learned from the failed cycle. They would also inform you about how they intend to change things up for the next one. They may want to change your medications or your pre-stimming protocol. No matter what they suggest, just make sure that you’re making sound medical decisions on how you want to proceed.
It is imperative to take good care of yourself after a failed IVF cycle. Ensure that you get all you need to remain calm as you prepare for the next round. Find healthy ways to cope with your stress levels and anticipation as you mentally prepare yourself for the upcoming cycle. All in all, no matter how disheartening a failed IVF cycle may be, there is still hope! It is essential to find healthy ways to cope with an unsuccessful first cycle as your mental state plays a massive role in your journey.
To boost egg health: Take adequate amount of omega-3 fatty acids, avocados and extra virgin olive oil. Eat plenty of seasonal fruits and vegetables as they contain important antioxidants that may enhance egg quality.
To assist embryo implantation: There’s research to show that whole grains like oats or brown rice may help embryo implantation. Vitamin E can also help, with nuts being the best natural food source.
To improve sperm health: Reduce exposure to toxins as this could negatively impact sperm quality – no smoking, drugs, or alcohol.
IVF related Queries – In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a kind of assistive reproductive technology (ART). The process includes taking out eggs from a woman’s ovaries and fertilizing them with sperm. After fertilization, this fertilized egg is called an embryo. The embryo is either transferred to a woman’s uterus or stored for future use.
There are various ways in which the IVF procedure is performed:
IVF is offered as an essential treatment for infertility in women. IVF can also be performed if you have certain medical issues. For instance, IVF might be a choice if you or your partner has:
Success rate in India ranges from 30% to 35%. Worldwide, the average IVF success rate is approximately 40% in young women. It has been observed that the chance of success rates also increases in women who are younger than 35 years of age. The success rate of this most commonly used reproductive technology is generally measured on the basis of live birth per embryo transfer. Live birth per embryo transfer is known as Live birth rate.
Zinc helps to maintain normal hormonal level. Include dairy products, grains, potatoes, and nuts, along with a few meat items in your diet.
Folic acid is essential to keep the embryo healthy and free of any developmental disorders. Peas, spinach, broccoli, kiwi, poultry products, and tofu are good source of folic acid for you.
Taking avocados improves ovulation within a woman – it increases the chance of having a successful IVF by 3.5 times.
Protein gives you energy and helps in development of body. It is recommended to take at least, 60 g on a daily basis. Seafood, meat, eggs, legumes and nuts are great source pf protein.
It takes between four and six weeks to complete one IVF cycle.
Normally, only one embryo is transplanted back into the womb. This process is known as single embryo transfer (eSET). This process is adopted to decrease the chance of multiple births.
It is advised to wait for two weeks after IVF before you do a pregnancy test. The reason behind this is it that it takes several days for the fertilized egg to implant into the womb and after that it has to produce enough pregnancy hormone that is hCG (human chorionic gonadotrophin) to be detected by a pregnancy test.
You can increase your chances of successful IVF by:
Once it is confirmed that you are pregnant, you’ll see your fertility specialist for continued blood testing, and an ultrasound to confirm that the pregnancy is progressing smoothly. Once the heartbeat of the fetus has been verified, consult with an obstetrician for the rest of your pregnancy. For more details about IVF related queries see our blog section.
How Vitamin D Affects Fertility – Vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is the primary type of Vitamin D in the skin. It is the form produced in the skin, and it tends to be found in some food and nourishing supplements. Prescription vitamin D is vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol). In general, research shows that we metabolize vitamin D3 more effectively than vitamin D2.
Vitamin D has been linked to a variety of health benefits. For women trying to conceive, it appears to be linked to better fertility, as well as a healthy pregnancy. Because of these potential benefits, female patients are screened for vitamin D deficiency as part of their initial screening process for pregnancy related complications.
The active form of Vitamin D (calcitriol) has numerous functions in female reproduction. Bound to its receptor, calcitriol can control the genes engaged with making estrogen. The uterine lining produces calcitriol because of the embryos as it enters the uterine cavity, in no time before implantation. Calcitriol controls a few genes associated with embryo implantation. When a woman becomes pregnant, the uterus and placenta keep on making calcitriol, which helps organize immune cells in the uterus, so infections can be fought without harming the pregnancy. Less vitamin D status has been related with certain pregnancy complications, for example, gestational hypertension and diabetes.
In humans, vitamin D deficiency has been shown to increase the risk of preeclampsia, pregnancy-induced hypertension, gestational diabetes, and lower birth weight. Vitamin D plays an important role in fertilization and pregnancy. Its exact role is still not understood, and the optimum blood concentrations are not yet known.
Vitamin D may likewise be a contributing element in the health of PCOS patients. In one examination seeing women attempting to conceive, 25(OH) D levels under 10ng/ml anticipated a diminished possibility of follicular development and a decreased possibility of getting pregnant.
Vitamin D may likewise demonstrate to have a significant function in fertility following up on both the ovary and the endometrium. At the ovarian level, vitamin D has been appeared to enhance ovulation.
For women attempting to conceive naturally, higher vitamin D levels are related with higher chances of conception. Studies likewise show that higher vitamin D levels in the follicular fluid may improve embryo implantation rate and the result of infertility treatments. Several studies have connected ordinary vitamin D levels with higher IVF pregnancy rates and live birth rates.
Keeping up a healthy vitamin D level isn’t just significant for women attempting to conceive. It can profit the male partner too. Studies have shown an immediate relationship between vitamin D levels and an improved ability of sperm to start a pregnancy, both during ovulation induction and planned intercourse. Normal vitamin D levels have additionally been connected to healthy semen quality and sperm motility (movement), which may help improve pregnancy rates.
Unexplained infertility is infertility of unknown cause. The reason of infertility is still not known even after tests such as semen analysis in the man and assessment of ovulation and fallopian tubes in the woman.
In unexplained infertility, any disorders or abnormalities are likely to be present but not diagnosed by current methods. The most possible cause of the problems could be:
The need of infertility diagnosis is normally occurs after a couple (with the female being under 35 years) has been trying to conceive for over one year with no success. However, for couples where the woman is of 35 years or older, infertility is diagnosed after they’ve been trying unsuccessfully for 6 months. When infertility is diagnosed, the doctor or fertility expert may suggest routine testing of your hormones, ovulatory cycles, anatomy, and even of your partner for male factor infertility (semen analysis). If you have unexplained infertility, no apparent problems will be found.
The diagnosis of unexplained infertility can be a very discouraging for couples who are trying to conceive. In this case when the reason for the infertility is not clear which symbolize that there is no solution for the problem. Thus the path for the pregnancy is not so smooth. When a couple knows the reason for their fertility problems, stress is often reduced.
Couples with unexplained infertility are still left with unanswered questions, sometimes causing feelings of guilt that they did something to cause the new fertility problems. It can be difficult to know which path to choose when the source of the problem can’t be determined. Despite all the difficult emotions, couples with unexplained infertility should realize that their diagnosis comes from a limitation of science and not of themselves. Current medical technology just isn’t yet capable of determining why they’re having problems getting pregnant.
There are a number of avenues you can explore to help you get pregnant with unexplained infertility, including:
Acupuncture: Many infertile couples choose acupuncture to help them conceive. Acupuncture may increase ovarian function and promote rich blood flow to the endometrium lining. Also, studies have shown more effectiveness of some fertility treatments when they are used in conjunction with acupuncture.
Intrauterine insemination (IUI): in this technique specially washed sperm are injected directly into the uterus at the precise timing of ovulation. This increases the chances of successful fertilization by getting the best quality and quantity sperm directly where it needs to be. Couples often try this procedure because it isn’t as expensive and time-consuming as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Fertility drugs: Even though there may not be a documented issue with ovulation, doctors sometimes prescribe fertility medications that induce ovulation. Examples include Clomiphene citrate (Clomid), gonadotropins, or FSH. A downside is that these drugs can increase your chances of having twins or multiples. Some of these fertility drugs may be used in conjunction with IUI or other ART.
Especially when the cause of infertility is unknown, improving your overall health is important. The most commonly suggested lifestyle changes to improve your fertility naturally are:
Eat a Nutritious Nutrient-Dense Whole Foods Diet: Changing the diet should always be the first thing anyone with unexplained infertility should do. Include fresh vegetables, fruits, raw seeds and nuts, whole grains, in your diet.
Fertility Herbs: It bring about healthy healing and change in the body. Some herbs are considered fertility superfoods which boost nutrition while supporting endocrine system function.
Omega Essential Fatty Acids aid the body in balancing weight, support body system function, and create a healthy environment for conception.
Thyroid and Infertility – The thyroid is a little gland situated in the neck. Its work, as an essential part of the endocrine system, is to control human body’s metabolism, the cycle by which the body converts what you eat and drink into energy through the hormones it discharges.
The thyroid gets a message from the pituitary gland by means of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and releases triiodothyronine (T3), thyroxine (T4), and calcitonin. While many know that an imbalance of TSH, T3, and T4 can cause weight or mood changes, it can also affect your menstrual cycle and fertility.
Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism can each adversely affect fertility both the ability to become pregnant and the ability to carry a fetus to term.
Abnormal TSH levels can interfere with ovulation and that when you have any sort of thyroid issue (without proper treatment), you will see a luteal phase (the last 50% of the cycle after ovulation) disturbance.
Thyroid dysfunction can affect fertility in following ways:
Although thyroid infection is often viewed as a women concern, around 33% of hypothyroidism cases emerge in men. Whenever left untreated, an underactive thyroid can prompt male infertility.
Studies show that low thyroid hormone levels in men can cause poor semen quality, low sperm count, diminished testicular capacity, erectile dysfunction and a drop in libido. Whenever hypothyroidism is diagnosed in a man to have fertility issues, bringing thyroid hormone levels once more into the normal levels for the most part restores erectile function.
Hypothyroidism can be easily treated, and once you get your thyroid levels back to a normal range, you can become pregnant. Treatment involves taking synthetic thyroid hormone in pill form. Though it may take a few months to determine the proper amount of hormone for you, once you and your doctor determine your optimal dosage, “you should be feeling yourself again and be able to conceive.
When hypothyroidism is the reason for infertility, taking thyroid medication will enable most women to conceive, from as soon as six weeks after treatment, according to a study. Many women who have a problem conceiving may have no apparent symptoms of hypothyroidism and only slightly elevated TSH levels, making it all the more important to have a TSH blood test if you’re having a hard time getting pregnant and don’t know why.
Treating hypothyroidism with medication not only improved conception rates, but also reduced miscarriages early in pregnancy, which can happen as a result of untreated severe hypothyroidism.
If you’re under the age of 35 and haven’t been able to conceive after a year of trying, or you’re over 35 and have been trying for six months, it’s a good idea to schedule a comprehensive infertility evaluation.
Because hormones play a critical role in every stage of conception and pregnancy, assessing thyroid function is an essential component of your infertility checkup. It’s especially important if you have a family history of thyroid disorders, or if you’ve ever experienced irregular periods or multiple miscarriages.
For women who are diagnosed with a thyroid disorder, medication is often all it takes to balance hormone levels and restore fertility. As always, your personal treatment plan depends on your exact diagnosis.
Semen Freezing Centers – Sperm freezing is the process of collecting, analyzing, freezing, and storing a man’s sperm. The sperm samples stored are later utilized for fertility treatments or given to different couples or people, including same-sex female partners. This general cycle is known as cryopreservation and sometimes is referred to as sperm banking.
The cryopreservation cycle includes:
Any individual who is healthy and has some sperm in their ejaculate is a good candidate for sperm freezing and children can also freeze sperm. Young children who have been diagnosed with cancer and have achieved pubescence are also acceptable candidates for sperm banking.
Those freezing for the reasons for sperm donation to sperm banks should be <40 years old, healthy, with good sperm quality, and without family backgrounds concerning for cancer or other genetic diseases.
Semen for cryopreservation is acquired by masturbation and must be brought to the ART (Assisted Reproductive Technology) research facility within 1 hour of ejaculation. Once in the research facility, an examination of the amount and quality of sperm is made and a small test vial is prepared. The remains of the sample are isolated into more different vials. The quantity of vials stored relies upon the total volume of the sample, and the number of mobile sperm in every milliliter. The whole freezing process is finished in around 3 hours. The next day, the test vial is thawed, and an assessment of the number and motility of the thawed sperm is performed.
Sperm freezing allows the sperm to be used in future fertility treatments such as:
Common reasons to choose to freeze sperm:
There are no risks or adverse effects to semen freezing normally (through masturbation). In case of surgical extraction is required, there are small risks involved, like with any medical procedure, such as, bleeding and discomfort.
Sperm freezing has been effectively utilized since 1953 to assist people with conceive healthy children. The cycle is safe, standardized and keeps on improving as technology advances.
The essential worry with sperm freezing is that not all sperm survive the freezing and defrosting process. However, as most semen ejaculations contain an appropriate number of sperm, the possibility of having enough healthy sperm for fertility treatment is exceptionally high. The ability of the surviving sperm cells to fertilize an embryo isn’t compromised during the freezing or defrosting process.
Cryopreservation is considered to have no time limit, and stored sperm as old as 20 years have been utilized to produce healthy infants. Find the best semen freezing centers here.
Recurrent Miscarriage – Miscarriages are normal, happening in 15-20% of all pregnancies, typically in the 1st trimester (up to 13 weeks). One or even two miscarriages are not by themselves characteristic of future infertility. In any case, they may leave patients concerned and questioning their capacity to have a live birth1.
Recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL), also referred to as recurrent miscarriage or habitual abortion, is historically defined as 3 consecutive pregnancy losses prior to 20 weeks from the last menstrual period.
There are numerous reasons for miscarriage, yet they are normally divided into two categories: early and late.
Recurrent early miscarriage (within the first trimester) is mostly because of hereditary or chromosomal issues of the embryos, with 50-80% of unconstrained losses having anomalous chromosomal number. Basic issues of the uterus can also play a part in early miscarriage.
Recurrent late miscarriage can be the consequence of uterine variations, immune system issues, an incompetent cervix, or premature labor.
Known causes of recurrent miscarriage include the following:
Genetics: A genetic issue with a developing embryo or a genetic condition that influences one or both the two parents may cause recurrent miscarriages.
Conditions influencing the uterus: The cycle of implantation is hormonally managed and requires a synchronized communication between the embedding embryo and the lining of the woman’s uterus (endometrium). Factors that change this relationship cause pregnancy loss.
Antibodies including lupus anticoagulant (LAC), anticardiolipin antibodies (ACA), and beta-II-glycoprotein antibodies are believed to promote miscarriage by causing clotting in the early placental circulation or by preventing optimal implantation. Treatment involves the use of low dose aspirin and other anti-clotting medications.
Other causes include:
Depending on the cause diagnosis for recurrent miscarriage can be done by the following:
Fetal Tissue Karyotyping
Although the diagnosis can be frustrating, treatment options to lower the risk of miscarriage are available. These options include:
How to get Pregnant with PCOD? – Polycystic ovary syndrome, or PCOS, is a hormonal condition that interferes with more than just your fertility; however, you may initially get a diagnosis when you’re attempting to get pregnant. This is on the grounds that it’s a typical and treatable reason for infertility in females. In PCOS, the ovaries become bigger than ordinary. These greater ovaries can have numerous cysts that contain immature eggs.
PCOS and infertility: They are firmly connected in various manners. The clearest one obviously is that most ladies with PCOS don’t ovulate routinely. Since the inability to ovulate commonly brings about irregular periods, getting your period can enlighten you so much about your fertility.
Living with PCOS and getting pregnant: It is challenging because our body doesn’t produce the hormones necessary for regular ovulation. Without these hormones, the egg inside the ovary does not fully mature. The follicle that holds the egg still grows and fills with fluid. However, there is no mature egg to rupture it, so it remains a cyst. The cysts with PCOS produce higher than normal amounts of androgens (male sex hormones), which block ovulation. Because no mature egg is released, ovulation fails to occur and the hormone progesterone is not made. This results in an irregular or absent menstrual cycle.
How to get pregnant with PCOD includes a portion of the very advances that females without PCOS should take for a healthy pregnancy:
If a low-GI diet seems right for you, and you can stick to it, then there is no harm in trying it out. However, if it isn’t a diet you can stick with, and you feel more comfortable with a basic low-calorie, low-fat diet, then go with that.
Some people with PCOS will need medications to treat the condition and/or to help them conceive.
Request that your primary care physician tests your insulin levels. In case you’re insulin-safe; taking the diabetes drug metformin can treat insulin obstruction and may assist you with getting in shape. It might likewise enable you to imagine. As indicated by the exploration, metformin may:
Clomid is the most ordinarily utilized richness drug in general and furthermore, the most usually utilized treatment for ladies with PCOS. Numerous ladies with PCOS will consider Clomid.
In the event that metformin and Clomid are not fruitful, your primary care physician may consider the medication letrozole. Likewise known by its image name Femara, it’s anything but a ripeness drug however is oftentimes utilized as one in ladies with PCOS. Letrozole is really a malignancy medicine. In any case, contemplates have discovered that it very well might be more viable than Clomid at animating ovulation in ladies with PCOS.
In the event that Clomid or letrozole isn’t fruitful, the following stage is injectable fruitfulness medications or gonadotropins. Gonadotropins are made of the hormones FSH, LH, or a blend of the two
On the off chance that the above alternatives don’t work, there might be different reasons why pregnancy can’t be accomplished and more intrusive treatment, for example, IVF might be required.
IVF includes a course of injections to stimulate the ovaries to produce numerous eggs. At the point when they’re adult the eggs are recovered in an ultrasound-guided strategy under light anesthetic. Sperm are added to the eggs in the research center for embryos to form.
A couple of days after the fact, the embryo is put in the uterus where it might embed and develop into a child. In the event that there is more than one embryo, these can be frozen for some time to use future if there is no pregnancy.
While IVF is safe, there are some conceivable health impacts to know about, including ovarian hyperstimulation conditions. This is an overreaction to the fertility medications that are utilized to stimulate the ovaries to produce numerous eggs. This can prompt stomach pain, nausea and vomiting, fast weight gain, and blood clots
How to become pregnant with irregular periods – It’s normal for women to have monthly cycles that may vary. One month it very well maybe 28 days, which is viewed as normal, and the following month it very well maybe 31 days, and the following 27. That is typical.
Periods are viewed as sporadic when they fall outside the “ordinary” range. An irregular menstrual cycle is one that is less than 21 days or more than 35 days. When including the days in your cycle, the main day of bleeding is the first day, and the most last day of the cycle is the first day of bleeding in your next cycle.
Irregular cycles may point to a subtle hormonal imbalance. You may still be ovulating every month, but your ovulation day may vary.
Here are some possible causes of irregular cycles that are also infertility risk factors:
If you are ovulating, but irregularly, you’ll need to make a special effort at determining your most fertile time. There are many ways to predict ovulation.
Ovulation predictor tests work a lot like pregnancy tests, in that you pee on test strips to determine when you’re most fertile. You don’t use the tests your entire cycle, but only around the general time you might expect to ovulate. When your cycles are irregular, that possible ovulation window may be longer than it is for other women.
Once your doctor has ruled out other medical conditions, they may prescribe fertility drugs to stimulate your ovulation.
The drug contained in Clomid and Serophene (clomiphene) is often the first choice because it’s effective and has been prescribed to women for decades. Unlike many infertility drugs, it also has the advantage of being taken orally instead of by injection. It is used to induce ovulation and to correct irregular ovulation by increasing egg recruitment by the ovaries. The drug letrozole is also used to induce ovulation3.
Dealing with irregular menstrual cycles can be distressing, Consulting a doctor for diagnosis and treatment is the first priority but there are habits that can also help you get pregnant with irregular periods naturally. Although these habits can’t replace medical treatment, they can help your fertility get back on track.
Get rid of these bad habits to improve your chances of becoming pregnant:
Research shows that eating healthy foods is a great way to get pregnant fast with irregular periods naturally.
These are some of the best foods for fertility:
How to Conceive with Ovarian Cyst – Ovarian cysts are liquid-filled sacs that can be found on or inside the ovaries. They are exceptionally normal, with numerous women getting them eventually in their life. Most are innocuous and cause no symptoms or agony, which is the reason they typically go undetected, vanishing over the long run without the requirement for clinical intervention.
Some ovarian cysts can be related with diminished fertility. In any case, it relies upon the kind of ovarian cysts you have.
Ovarian cysts that can influence your fertility include:
If your doctor suspects that you may have a cyst, they will begin by completing a pelvic exam to look for swelling. Since cysts do not often require treatment, there are a number of different options the doctor can choose between:
Most ovarian cysts disappear on their own and don’t need any treatment. In rarer cases, such as in the case of an ovarian cyst rupture or ovarian torsion, the following treatment may be warranted:
Having a cyst on an ovary does not usually affect one’s chances of becoming pregnant, which is why doctors will typically only investigate further if a couple has been trying to conceive naturally through regular intercourse for a year, but have not yet been successful in falling pregnant.
There are several things you can do to maximize your chances of becoming pregnant naturally:
That’s all about how to conceive with ovarian cyst.
Laparoscopy for infertility is a minimal invasive surgical technique that utilizes a laparoscope (a fiber-optic tube with light and camera) inserted through at least two minor cuts, frequently in the belly button. The specialist can then visually analyze the pelvic reproductive organs and the pelvic cavity.
The technique might be performed under general anesthesia or local anesthetic and generally takes 30 to 45 minutes. The abdomen is inflated with gas (carbon dioxide or nitrous oxide injected with a needle) to move the organs from the stomach wall so they are visible during the technique.
When the abdomen is expanded, the laparoscope is inserted through the small cuts. The specialist sees the interior of the pelvic cavity on a video screen transmitting the pictures from the camera.
The specialist will search for potential causes for infertility. These could be:
Possible reasons your doctor may recommend diagnostic laparoscopy include:
Post your medical procedure; you may get discharged the same day if there are no complications. Your primary care physician will recommend rest for a few days. However, you may take a long time to recover totally. You will be given different medications for a quick recovery, which may include antibiotics and painkillers.
Like any medical procedure, laparoscopy for fertility has expected risks. Just 1-2 percent of patients who go through laparoscopy for diagnosing or treating fertility experience a complication, including sedation related issues. Minor difficulties include disease and skin aggravation at the incision site.
More extreme complications may include:
Hysteroscopy in Infertility – Hysteroscopy is a minimally invasive technique used for the diagnosis and treatment of uterus health conditions. During the technique, the doctor inserts a hysteroscope (a lighted, telescope-like instrument with a camera toward one side) through the vagina to analyze the cervix and uterine cavity. Small instruments can be passed through the hysteroscope to perform biopsies or eliminate irregularities from the uterus that are identified.
A hysteroscopy doesn’t need a cut or incision. An indicative hysteroscopy can take as less as 30 minutes, however in the event that the doctor needs to perform a procedure, for instance eliminating a fibroid, the hysteroscopy may take longer. Diagnostic hysteroscopy can frequently be performed in a medical office, yet more complex procedures are best performed in a clinically equipped facility.
Hysteroscopy is valuable in diagnosing and treating conditions that can cause infertility. These conditions may include uterine fibroids, polyps, scarring and birth defects in the structure of the uterus, for example, an uterine septum. Hysteroscopy is likewise used to:
Diagnostic hysteroscopy permits the doctor to check the size, shape and lining of a woman’s uterus to diagnose any abnormalities that might be affecting fertility or causing other gynecologic problems.
Operative hysteroscopy might be performed to treat an abnormal condition diagnosed during diagnostic hysteroscopy. Small instruments can be passed through the hysteroscope to treat problems, for example, endometriosis, uterine polyps, and fibroids, or adhesions.
Just like any medical procedure, you could have some complications from a hysteroscopy, including:
If you experience symptoms like a fever, severe abdominal pain, or heavy bleeding after the procedure, call your doctor immediately or go to the emergency room.
Embryo freezing is a process that permits individuals to store embryos for sometime in the future. An individual can also freeze eggs, which are not fertilized. An embryo is developed after fertilization and the cells begin to divide. Physicians can freeze and store unused embryos (fertilized eggs) created during IVF, which may include intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), using a process called cryopreservation.
Fast cooling convention (vitrification) includes media containing a higher concentration of cryoprotectants and has a moderately lot more limited freezing time. The fundamental concern when freezing an embryo is the development of ice between the cells. This can be effectively avoided by a profoundly skilled embryologist.
Slow cooling includes seeding where the cryopreservation straw is physically moved by cold forceps dipped in liquid nitrogen further away from the embryo to start ice development which spreads to the rest of the solution containing the embryos. This prevents harm to the embryos. Most centers today apply vitrification for freezing embryos.
During this method, the frozen sperm/oocytes/embryos are thawed (de-frozen) to room temperature, noticed for further development, and afterward moved into the patient’s uterus after stimulating endometrial development. At the time of embryo substitution, the straws are taken out from the liquid nitrogen and set in a water shower at room temperature before re-hydrating with unique media. Toward the finish of re-hydration, the embryos are cultured in media inside the carbon dioxide incubators and permitted to grow further either to day 2 or blastocyst prior to transfer.
Research shows that the freezing and thawing of embryos does not harm subsequent babies made through IVF. The length of time the embryo was stored does not affect IVF success rates.
With improving technology, the difference in pregnancy rates between the frozen embryos and fresh is negligible. In addition, the stimulation process with frozen embryo transfer is gentler, with hormone levels closer to normal in the woman, which may also improve pregnancy rates.
Any ice crystals formed during the slow freeze process may cause damage to an embryo while thawing. This is one of the reasons vitrification is the preferred cryopreservation technique. Research shows that there is no increase in the risk of birth defects among children born from frozen embryos compared with normal births.
Endometriosis is a condition wherein tissue like the uterine lining (endometrium) grows somewhere else in the body. Pelvic pain is the most common indication of endometriosis, yet a few women with the condition may likewise encounter infertility.
Endometriosis may develop outside of your uterus, ovaries, and tubes and even on your bladder or digestion tracts. This tissue can irritate structures that it contacts, causing pain and adhesions (scar tissue) on these organs.
Symptoms can vary with some women not having any at all, and others having very severe pain. The most common symptoms are:
On the off chance that you have endometriosis, it might be more difficult for you to get pregnant. Up to 30% to 50 % of females with endometriosis may encounter infertility. Endometriosis can impact fertility in different ways: distorted anatomy of the pelvis, adhesions, scarred fallopian tubes, inflammation of the pelvic structures, altered immune system functioning, changes in the hormonal environment of the eggs, impaired implantation of a pregnancy, and altered egg quality.
At the point when endometrial tissue wraps over your ovaries, it can block your eggs from releasing. The tissue can obstruct sperm from making its way up your fallopian tubes. It can likewise prevent a fertilized egg from sliding down your tubes to your uterus.
In case of difficulty getting pregnant with endometriosis you may wish to consult a fertility specialist. Treatment options for endometriosis related infertility include:
The success rates of IVF are 50 percent for women who don’t have endometriosis. But many women with endometriosis have successfully gotten pregnant thanks to IVF treatments. IVF is often recommended for women with moderate to severe endometriosis, or for women whose bodies haven’t responded to other treatments.
Egg banking, also known as oocyte cryopreservation, is a moderately new strategy for fertility protection where a developed, unfertilized egg is retrieved from a female, frozen and stored for later use.
Egg banking includes a female deciding to have eggs retrieved from her ovaries, frozen to preserve their viability and put away until she is ready to utilize them in a future in vitro fertilization (IVF) treatment to achieve pregnancy.
Egg freezing and egg banking can be utilized to preserve fertility in patients having aggressive medical treatments, for example, chemotherapy, or in patients who wish to protect their fertility presently to begin a family later.
Egg freezing is achieved through a new IVF cycle, avoiding egg treatment in vitro.
Egg banking increases opportunities for women going through cancer treatment who preserve their fertility. In the event that they have a partner, they could go through a stimulation and retrieval cycle, developing embryos, and freeze them for some time in the future. They could do likewise without an available partner, in the event that they willing to utilize donor sperm to develop embryos. This would ensure them hereditary offspring, yet with a missing sperm donor father. In the event that they come up short on a partner and ability to utilize a sperm donor, egg freezing would empower as it both secures their fertility and gives them a decision over the genetic father of their post-treatment children. A comparable need may emerge with women with hereditary illnesses or different conditions, for example, premature ovarian failure, who had not yet found a spouse yet needed to ensure they have healthy eggs at a later point in their life for reproduction.
Egg freezing carries several risks to the woman or couple, including:
Pregnancy with Small Uterus – Most females don’t realize that they have a little uterus until the time they get pregnant. At the point when a female presumes that she is pregnant and goes to a specialist, a gynecological test or ultrasound may bring this information on (having a small uterus) and can be a reason for colossal concern. On occasion, the specialist’s language may likewise impart fear. In any case, it is consistently essential to get to the bottom of it and comprehend the medical issue appropriately.
In certain females, the uterus can be bigger than normal or considerably smaller. However, it should work fine. A female’s general body additionally plays a significant overseeing factor for the uterus size. Hence, females who are mysteriously thin or have a small body face have higher odds of having a small uterus.
Small uterus can either be formed during the developing years of a girl, caused by a medical procedure or therapy or can be a congenital condition. This frequently causes infertility or obstetric issues in the life of a female. This incorporates failure to conceive, issues in delivering a healthy child, unpredictable periods, or no periods at all.
On the off chance that you become pregnant with a small uterus and this is entirely conceivable either normally or with regenerative help, your doctor may recommend more frequent visits and ultrasounds to screen the infant’s development.
Your doctor may likewise need you to have a cervical cerclage or arrangement of a cervical ring or pessary if you have cervical shortening. This may assist with diminishing the risk of premature delivery.
Your doctor may likewise recommend certain medications known as tocolytics, to decrease the probability that preterm delivery will happen. Tocolytics loosen up the uterus and decrease preterm labor contractions.
One of the vital elements to be considered to effectively conceive with a small uterus is the epithelium. Increased blood flow can help with its development. the doctor may sometimes prescribe a pregnant woman to go for hormonal therapy to increase the chance of conception.
Any sort of hormone treatment affects the outside genitalia. Hormone treatment might be proposed for women who experience the ill effects of a condition where the uterus, as well as the genitals, are immature, causing an imbalance of different hormone levels inside the body. Named hypoplasia, it could likewise demonstrate the presence of different diseases also. Undertaking hormonal treatment in such a case could, indeed, makes the situation worse.
Defining the uterus as “small” is not enough for doctors to make a proper decision. Further diagnosis is necessary to determine the actual condition. It could be hypoplasia, where the uterus is small due to hormonal issues. Aplasia could be a cause as well, where the uterus is the same as that of a newborn child or even absent. Another condition could be infantilism, where the uterus is not larger than 55mm. Any kind of treatment method to increase the size of the uterus takes a good amount of time. Using hormonal medication is a common method for women diagnosed with hypoplasia. In certain cases, being involved in sexual activity regularly can be beneficial as well, and could cause the uterus to increase in size gradually.
At times, proper intake of nutrients and minerals could make conception possible. On the off chance that you are pregnant and have a little uterus, you can choose a vitamin treatment. It utilizes certain liquid preparations which, when used every day, can be very valuable.
IVF is the process of fertilization by extracting eggs, recovering a sperm sample, and afterward physically joining an egg and sperm in a laboratory. The embryo(s) is then moved to the uterus. As indicated by the Society of Assisted Reproductive Technologies (SART), the success rate of giving birth to a live child after IVF is as per the following:
Live Birth Rate: Live birth rate is the number of infants born divided by the number of cycles started to accomplish the birth. Remember that this information is generally dated, and patients should remember that doctors are continually refining and improving IVF.
Implantation and Pregnancy Rates: It permits a person to see the number of patients got a positive pregnancy test, the number of clinical pregnancies (checked by ultrasound), as well as the number of miscarriages.
Cycle characteristics: Cycle characteristics include average (mean) number of embryos transferred and the percentage of patients deciding on elective single embryo transfer (eSET).
Common factors that determine the success of IVF includes the following:
Women age and utilization of own eggs are significant IVF success factors to consider. While young females have higher odds of IVF success, factors that decrease the odds of IVF success incorporate being a older woman with less eggs and the lower quality of a older woman eggs. The live birth IVF success rate for women under 35 who start an IVF cycle is 40%. However, women over age 42 have a 4 percent achievement rate.
More IVF success factors to consider incorporate whether you were pregnant already and in the event that it was with the same partner. In the event that you were pregnant beforehand with the same partner that is as of now going through IVF treatment, there is a more prominent chance of IVF success. Factors, for example, a background marked recurrent miscarriages or a different partner may decrease the odds of IVF success.
While some male infertility issues do affect IVF success, factors like uterine irregularities, exposure to DES or fibroid tumors likewise declines the probability of success with IVF.
Important to know: IVF success factors are reliant on ovulation. Ovarian dysfunction, similar to high FSH levels which demonstrate a low ovarian reserve, may diminish the chance of IVF success. Variables that may bring down pregnancy rates and decrease success with IVF include requiring a lot of ovulation stimulation drugs.
Whenever the two partners are infertile with lower chances for IVF success, factors, for example, the time you have been infertile is imperative to consider. The chances of IVF success decline with the amount of time a couple has been infertile.
Donor eggs are a critical consideration, particularly if the women are more than 35-40, as there might be a higher rate of IVF success. Factors, for example, egg quality and age of donor are significant. Utilizing donor eggs from young women may build the chances of pregnancy for women more than 40. 2011 discoveries show a 55 percent live birth achievement rate with a new donor egg/embryo transfer.
The fertility clinic you decide for the IVF treatment can enormously influence your IVF success. Variables to consider while assessing the success rate of the clinic include:
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is a fertility treatment in which an egg is implanted by sperm outside of the female’s body. The egg is embedded in the female’s uterus after a certain number of days (2-6) of growth.
IVF can be used in a variety of situations, including infertility, reproductive surrogacy, and . menopause.
It is the fact that menopause is an obstruction to further conception, IVF has allowed females to have a baby at age of 50 and above. IVF likewise gives females with beginning early menopausal a possibility. Females, whose uteruses have been appropriately prepared, can get Pregnant from an egg of an egg donor. Even after menopause initiates, the uterus is very fit for carrying an effective pregnancy.
In females who are of childbearing age, there are five stages to IVF: stimulation, egg retrieval, insemination, and fertilization, embryo culture, and embryo transfer. However, on the grounds that females who have just experienced menopause are not delivering eggs, they don’t have to experience the initial two stages, and will rather need to utilize eggs from an egg donor.
Getting pregnant through IVF, similar to all pregnancies, accompanies risks. Yet, in case you’re generally healthy, an IVF-instigated pregnancy after menopause won’t really carry any new complications.
Pregnancy-related risks like high blood pressure, preeclampsia, infections, and preterm labor are the most common complications, but some women who try IVF after menopause don’t have to worry about particular problems linked to their older ages during pregnancy.
Since a youthful woman’s egg is used, the risk of chromosomal abnormalities is reduced. .
Donor egg and embryo transfer gives the most reasonable conceptive choice for older women who are either perimenopausal or menopausal and remains the best treatment of choice for patients of cutting edge reproductive age.
Oocyte donation from young donor reduces the issues of decreased ovarian reserve and expanded aneuploidy risk that goes with propelling age, and results in altogether higher pregnancy rates than standard IVF regimens.
Females over 45, even as old as 55, may achieve pregnancy rates similar to young females using their own eggs. When donated oocytes are used, recipient age has no effect on cycle outcomes, with fertilization rates, embryo implantation rates, and continuous pregnancy rates comparable to younger females.
Pregnancy during perimenopause or postmenopause, while possible, poses some health dangers.
These hazards, which are similar to pregnancy risks for women over the age of 35, include:
As a woman ages, previous ailments can increase health risks for pregnancy and delivery. So prior to thinking of getting pregnant after menopause, consult a doctor who can assess your general health for IVF after menopause.
IUI Treatment – Intrauterine insemination (IUI), a sort of manual semen injection is a method for treating infertility. Sperm that have been washed and concentrated are placed in your uterus directly around the time your ovary discharges at least one egg to be fertilized.
The hope for result of intrauterine insemination is for the sperm to swim into the fallopian tube and fertilize the egg, resulting in conception. Depending upon the type of infertility, IUI can be facilitated with your typical cycle or with fertility medications.
IUI is utilized to treat numerous kinds of infertility and is regularly done in various cycles until pregnancy is accomplished or another treatment is attempted.
Cycles of IUI may be recommended to treat any of the following infertility situations:
IUI is not recommended for those with:
Insemination is performed at the time of ovulation, usually within 24-36 hours after the LH surge is identified, or after the “trigger” injection of hCG is administered. Ovulation is anticipated by a urine test kit or blood test and ultrasound.
In the case of husband insemination, the male produces a sperm sample, at home or at the facility. The sperm is then prepared for IUI. Sperm from the male partner or donor are washed or separated.
Partition selects out motile sperm from the man’s discharge and concentrates them into a small volume. Sperm washing purifies the sperm of any poisonous synthetic compounds which may cause adverse responses in the uterus. The doctor utilizes a delicate catheter that is passed through a speculum directly into the woman’s uterus to deposit the semen at the time of ovulation.
There is a small risk of infection following the IUI procedure. Your doctor will use sterile instruments, so infection is very rare.
If medications are used to induce ovulation, there is a risk of pregnancy with multiple babies. Since fertility medications increase the likelihood that more than one egg will be released, they also increase the likelihood of pregnancy with multiples.
Sometimes the ovaries over-respond to fertility medications (particularly the medications given as injections) and a condition called ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome may result.
Each couple will have an different response to IUI, and it very well may be hard to anticipate its success. Various factors influence the result, including:
Pregnancy rates following IUI are differed dependent on your need behind requiring fertility treatment. Success rates for IUI will in general diminish in women beyond 40 years old, and in women who have not gotten pregnant after three cycles of IUI.
Fallopian tube blockage – Fallopian tubes are female reproductive organs that join the ovaries and the uterus. Consistently during ovulation, which happens generally in the middle of a monthly cycle, the fallopian tubes deliver an egg from an ovary to the uterus.
Conception likewise occurs in the fallopian tube. In the event that an egg is fertilized by sperm, it travels through the tube to the uterus for implantation.
In the event that a fallopian tube is blocked, the entry for sperm to get to the eggs, as well as the way back to the uterus for the fertilized egg is obstructed. Common caused behind blocked fallopian tubes include scar tissue, infections, and pelvic adhesions.
Most women with tubal blockage are asymptomatic. Frequently they don’t understand their fallopian tubes are obstructed until they consult a doctor for infertility, however women with broad tubal damage may encounter chronic pelvic pain.
Blocked fallopian tubes are a typical reason for infertility. Sperm and egg meet in the fallopian tube for fertilization. An obstructed tube can keep them from joining.
If both tubes are completely blocked, pregnancy without treatment will not be possible. In the event that the fallopian tubes are partially blocked, you can conceivably get pregnant. However, the risk of an ectopic pregnancy is enhanced in that case.
The most widely recognized reason for blocked fallopian tubes is Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). PID is the result of sexually transmitted disease, although not all pelvic diseases are related to STDs. Additionally, regardless of whether PID is not, a history of PID or pelvic disease expands the risks of blocked tubes.
Other expected reasons for blocked fallopian tubes include:
There are three key diagnostic tests for blocked fallopian tubes:
It may be possible to open blocked fallopian tubes surgically. However, this depends on the extent of the scarring and where the blockage is.
Surgery aims to open the fallopian tube using one of the following methods:
Most surgeons will carry out the procedure using keyhole surgery.
Age for IVF treatment – Infertility is a complicated issue that affects up to 15% of couples who are attempting to conceive. Depending on the individual circumstance, different infertility factors might be treated through in-vitro fertilization (IVF). IVF is usually effective, particularly for women under age 35 or for those who use donor eggs.
As indicated by the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology, achievement rates for IVF decrease drastically after age 37, making age the main factor for women who want to pursue pregnancy utilizing their own eggs. After age 43, donated eggs from younger women are frequently needed for effective pregnancy.
As a woman ages, the excess eggs in her ovaries likewise age, making them less capable of fertilization and their embryos less fit for implants. Just 12 percent of the 300,000 eggs a female is born with remains at age 30, and just 9,000 eggs remain at age 40. Females who are perimenopausal ordinarily react ineffectively to ovarian stimulation medication and their live birth rates with IVF treatment are essentially lower than with younger females.
As we all know, there is no “guarantee” in medical procedures – every doctor can authenticate this fact. Thus, the only guarantees we can discuss in IVF are monetary and financial in nature, that is, a reimbursement guarantee in the event that the IVF program doesn’t end with the desired outcome.
Money back guarantee plans are advertised since insurance covers just 15% to 25% of IVF costs. IVF is a high technology clinical help with costs going from $6,000 to $12,000 (4 to 8 Lakhs INR). In spite of the fact that the IVF live-birth rate per egg recovery for young patients has doubled in the previous decade, to roughly 40%, numerous women don’t conceive on their first attempt, and it is difficult to guarantee any clinical result with the technology.
After three IVF cycles, including utilization of frozen embryos from those cycles, the probability of having a child increases to 60% to 90% in women younger than 40. On the off chance that IVF fails, in any case, a generous reimbursement may help a couple to adopt (which can cost $20,000 to $40,000), attempt different types of assisted reproduction, (for example, a gestational carrier, which expenses up to $60,000), or recover part of their original investment.
The financial guarantee is really not determined on the measure of total money that is paid during the beginning of the treatment cycle. Rather, the sum is a variable percentage that is really a portion of the complete treatment cost acquired.
The age of the woman act as the principle determinant. The amount of money reimbursed and the age of the woman is inversely proportional to one another. The older the woman, lesser the reimbursement is given.
IVF Refund and IVF Money Back Guarantee projects can be additionally grouped into:
An embryo transfer is a part of IVF procedure in which a fertility specialist uses an ultrasound to guide a catheter containing the IVF-produced embryo(s) to transfer the embryo(s) directly into the uterus. The process of embryo transfer takes only a few minutes. The process does not involve anesthesia and only short recovery period is required. Prior to the transfer, embryos are graded and the type of grading depends on the stage of the embryo. For cleavage stage embryos, typically on day three, the number of cells and a grade (A – D) will be assigned. For blastocysts, there will be a number and two letters assigned. The number refers to the amount of expansion of the fluid (the “cyst”) in the blastocyst. The two letters (A – D) that follow refer to the inner cell mass (destined to become the baby) and the trophectoderm (destined to become the placenta), respectively. Cells from an embryo can also be tested for genetic anomalies prior to an embryo transfer. Scientists have a choice of two genetic tests for embryos. In preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD), an embryologist removes a group of cells to test for a specific genetic abnormality, such as cystic fibrosis. Preimplantation genetic screening (PGS) tests for the proper makeup in all chromosome pairs, as missing or additional chromosomes lead to disorders and diseases. An example of such a disorder is Down syndrome, in which there is an extra chromosome in pair number.
A blastocyst transfer includes developing embryos in a laboratory for five days before transferring them into the uterus. When the embryo has reached the blastocyst stage (day five), it is more fully developed with multiple cells. At this point the embryo resembles the stage of a natural embryo when it enters a uterus for implantation, which increases the chances of attaining a successful pregnancy. However, it is not necessary that all embryos are able to develop to the blastocyst stage. Studies show that blastocyst transfers result in higher implantation and pregnancy rates as compared with cleavage stage embryos. Blastocyst transfers may be of particular benefit for patients who develop many good quality embryos, who have failed to achieve a pregnancy with a day three transfer in the past, or who have poor quality embryos at day three.
A cleavage stage embryo transfer refers to embryos that are transferred at an earlier stage of development when they have fewer cells, typically six to eight, and occurs on day two or three after fertilization. Cleavage refers to the division of the cells in an early developing embryo. Cleavage stage embryo transfer is a good option for patients who have fewer good quality embryos. Also, transfer on day three is less risky than allowing the embryos to go to day five.
IVF and embryo transfer is required in cases where there is difficulty in natural conception or difficulty occurring. There are many reasons for embryo transfer, including:
Around 2 or 3 days before the embryo transfer, the doctor will choose the best eggs to transfer to the womb. There are many processes available to aid selection, though non-invasive methods such as metabolomic profiling are being tested. Metabolomic profiling is the process of selecting the most beneficial eggs based on a number of different factors. This could limit the need for invasive procedures in the future. These eggs will then be fertilized in a lab and left to culture for 1-2 days. If many good quality embryos develop, the ones that are not going to be transferred can be frozen.
A follow-up appointment after 2 weeks to check if the embryo has implanted well and the transfer was successful. After the procedure of embryos transfer, women may experience some cramping, bloating, and vaginal discharge.
The IVF Treatment cost in India or anywhere else in the world generally depends on the infertility workup. Therefore, it may vary from person to person. If your friend or relative was lucky enough to have a baby by going through two IVF cycles, you may be fortunate by conceiving in one IVF cycle itself. Or perhaps a simple laparoscopy procedure might be enough to cure your infertility. The IVF cost in India or around the world is rising up as a more and more modern diagnostic test, and treatment methods are being used to aid and facilitate infertility treatments cost. Because of this, there is no upper limit to the amount of money one can invest in their quest for a child.
According to several online sources, the cost of IVF in India varies greatly by city. The most basic IVF package that does not include the technique like monitoring, medications, ICSI, FETs, genetic testing, or other add on services that are either necessary for all (like medications and monitoring) or some (like ICSI, FETs and genetic testing).
| City | Indian Rupee |
|---|---|
| Delhi | 1,10,000 to 2,50,000 |
| Kolkata | 1,00,000 to 2,20,000 |
| Banglore | 1,40,000 to 2,50,000 |
| Chennai | 1,45,000 to 3,00,000 |
| Nagpur | 1,25,000 to 2,80,000 |
| Pune | 1,35,000 to 3,00,000 |
| Hyderabad | 1,60,000 to 2,80,000 |
Similar to the other fertility based clinics in foreign countries, when quoting IVF costs to patients, clinics in India offer pricing for a very basic, no-frills IVF cycle that doesn’t include many things that may indeed be required in order to do the IVF treatment. Most basic IVF packages include egg retrieval, sperm preparation, conventional IVF fertilization, and one fresh IVF transfer. These services alone don’t support a viable IVF cycle for many patients. Fertility medications, monitoring, and retrieval anesthesia are necessary for most if not all patients, and there’s often an extra fee associated with each.
| Component | Required | Indian Rupee |
|---|---|---|
| Monitoring | Yes | 20,000 |
| Medications | Yes | 80,000 |
| ICSI | For Some | 1,50,000 |
| Assisted Hatching | For Some | 20,000 |
| Cryopreservation | For Some | 30,000 |
| FET | For Some | 80,000 |
| Preimplantation Genetic Testing | For Some | 2,00,000 |
Most low-cost IVF programs require you be out of the country or away from your home and job for the entirety of the IVF treatment (estimated 3-7 weeks). So, there is the actual cost of travel (airplane), lodging, and meals, but also the added inconvenience of a longer stay, missed work, and safety during your stay. Some cities in India are not as safe as others, which should also be a consideration when choosing a destination for treatment. And since IVF isn’t always successful the first go around, it may take more than one trip abroad to bring home a baby. Depending on where you’re traveling from in the U.S. and to in India, travel costs can range quite a bit. Whether you’ll be staying in a hotel or renting another longer-term lodging also will affect the cost. Medical visas are only around $100 per person.
Male infertility means a man not being able to become a father. Also, infertility is the inability of a sexually active without using any contraceptive methods to achieve pregnancy in one year. Male infertility is often referred to when the cause of the fertility problem is found in the man. In most cases, the causes of male infertility are either the semen is unable to reach the egg, this is known as obstructive or the semen is of poor quality, this is known as non-obstructive. In approximately 30-40% of patients, no male factor is found (idiopathic/unexplainable male infertility). It is estimated that male infertility is found in approximately half of all infertile couples.
Infertility as such doesn’t cause any particular type of symptoms in men. But in case if the infertility is caused by any medical or surgical condition or may be due to low hormone levels, the patient may have certain symptoms. The symptoms will depend on the cause of infertility. A condition that affects your testicles may cause:
Any disorder or problem in the prostate gland or epididymis (the tube that carries sperm from the testicles), may cause:
The most common reason for male infertility is a problem with sperm. It may be that:
Patients may have all these three problems at the same time. In some men, there are no or nil sperm in their semen. This condition is commonly known as obstructive azoospermia. In this condition, the tubes that carry sperm from your testicles to your penis (seminal ducts) are blocked. You may be born with this or you may develop it after an infection, bladder neck surgery, or may be due to scarring after an inguinal hernia repair.
If a man has the disease condition of hypogonadism, he may not able to produce any hormone such as testosterone. This may result in low sperm count, or the person can’t get an erection and have low sex drive (libido).
There are many problems that can affect how you ejaculate (release semen during sex).
Having sex every two to three days will maximize the chance of pregnancy by making sure you’re having sex during your partner’s most fertile time of the month.
If your scrotum (which contains your testicles) is too warm, this may reduce sperm quality. Loose-fitting underwear may help to lower scrotal temperature.
Some jobs involve working with hazards that can affect your fertility. These include heat, metals, pesticides and X-rays.
Having trouble conceiving can be stressful. This may affect your sex drive or your relationship, meaning you have sex less frequently.
If you have low testosterone levels (hypogonadism), your doctor may suggest gonadotrophin injections to improve your fertility. These trigger your body to make testosterone and produce sperm. If you have retrograde ejaculation, sperm are ejaculated backward into your bladder instead of through your urethra and out of your body. Your doctor may prescribe medicines such as pseudoephedrine to help close the opening to your bladder. Medicines such as sildenafil (Viagra), tadalafil (Cialis) may be helpful if you have trouble getting an erection.
Having no sperm in your semen is often caused by a blockage in the tubes that take sperm from your testicles to your penis. Surgery may be possible, to remove the blockage and improve your fertility.
Eat plenty of foods rich in vitamin C and other antioxidants: These nutrients help prevent sperm defects and boost motility.
Include Zinc in your food: Deficiency of Zinc may lead to clumping of zinc which may lead to infertility. So take enough amount of zinc in the diet.
Incorporate Folic acid: Folic acid is critical for male fertility. Try to take at least 400 micrograms of Folic acid daily to produce healthy sperm.
Limit alcohol intake: wine, beer, and hard liquor may reduce sperm count and abnormally shaped sperm. Try to cut down the daily intake to increase the chance of conceiving.
Reason for IVF Failure – In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a perplexing arrangement of techniques used to help with fertility or prevent hereditary issues and help with conception.
During IVF, developed eggs are gathered (recovered) from ovaries and fertilized by sperm in a lab. At that point, the prepared egg (embryo) or eggs (embryos) are moved to a uterus. One full pattern of IVF takes around three weeks. Once in a while, these means are part of various parts and the cycle can take longer.
IVF treatment doesn’t generally work effectively. More youthful ladies have a higher possibility of IVF achievement, with the achievement rate for ladies under 35 at 40%. IVF can fall flat for some reasons, and the odds are that it is totally out of your control.
The human egg is liable to get harmed that can deliver it nonfunctional. The oocyte is liable to harm because of the presence of free radicals, reactive oxygen species and different results of digestion that happen inside the ovary as a female ages. Numerous ongoing examinations have exhibited that somewhere in the range of 25% and 40% of all oocytes are chromosomally anomalous. This number clearly increments as female ages.
Embryologists select embryos to transfer dependent on three essential standards: cell stage, embryo grade and the pace of cell division. We know from studies performed that on day three, embryos that have developed to at least the 6 cell stage have a greatly improved visualization for progress than embryos that have 5 or less cells.
At times female ovaries don’t react to the fertility drugs emphatically enough to develop numerous eggs. Particularly if a female is more than 37 or has higher FSH levels she may not deliver enough eggs to bring about various embryos for screening and possible implantation. Odds are higher that IVF will bomb when this occurs. Your conceptive endocrinologist will assess what occurred and may make changes to your fertility drugs for the following IVF cycle.
Numerous fertility centers expect women to quit smoking in any event three months prior to beginning IVF treatment. Women who smoke need twice the same number of IVF cycles to consider and are substantially more liable to lose than women who don’t smoke. Women who are overweight or underweight are less inclined to have successful IVF treatment. The primary concern is, keep up a healthy weight. On the off chance that you are overweight, losing as little as 10% of your body weight can have a beneficial outcome in your capacity to get pregnant4.
The sperm plays a significant fertilisation of the female egg and to do as such, they should be healthy, motile, and adequate in amount.
The eggs and sperm both have explicit receptors on their surface that take into consideration their association. During this contact, compounds delivered from the sperm head make an opening in the external films of the egg, permitting it to enter through.
However chromosomal elements, sperm are typically not among the explanations behind failure of IVF in light of the fact that any quantitative or subjective issues with the sperm are handily distinguished during semen investigation and the patients are then given the choice of intracytoplasmic sperm infusion (ICSI) or IVF with contributor sperm.
A more uncommon reason for IVF failure, this circumstance happens when the sperm neglects to enter and prepare the egg.
Understanding what causes IVF failure is the initial move toward preventing it. The following and apparently most significant advance is realizing how to dodge it with individualized conventions, including pre-implantation genetic testing, or PGT.
Fibroids are noncancerous developments of the uterus that frequently show up during childbearing years. Additionally called leiomyomas or myomas, uterine fibroids aren’t related with an expanded danger of uterine disease and never form into malignant growth.
Fibroids range in size from seedlings, imperceptible by the natural eye, to cumbersome masses that can contort and grow the uterus. You can have a solitary fibroid or various ones. In outrageous cases, numerous fibroids can grow the uterus so much that it arrives at the rib confine and can add weight.
Numerous women are ignorant they have fibroids since they don’t have any symptoms.
Women who do have symptoms (around 1 of every 3) may insight:
There are a few tests that make possible to confirm fibroids and decide their size and area. These tests can include:
Specialists may build up a treatment plan depends on your age, the size of your fibroids, and your general health.
Home remedies and natural treatments
Certain home remedies and natural treatments can positively affect fibroids, including:
Dietary changes can help also. Stay away from meats and fatty nourishments. All things considered, decide on nourishments high in flavonoids, green vegetables, green tea, and cold-water fish, for example, fish or salmon.
Dealing with your feelings of anxiety and losing weight in case you’re overweight can likewise profit women with fibroids.
Drugs to control your hormone levels might be prescribed to shrink fibroids.
Gonadotropin-delivering hormone (GnRH) agonists, for example, leuprolide, will cause your estrogen and progesterone levels to drop. This will ultimately stop period and shrink fibroids.
GnRH antagonists additionally help to shrink fibroids. They work by preventing your body from delivering follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH). Examples include:
A failure to IVF is no more a limitation. The donor egg IVF technique will allow an infertile woman with abnormally functioning ovaries to give birth to her child. This technique includes fertilization of the egg of another woman and the sperm of the intended father unless the sperm donor is not involved. Then the fused egg and sperm (embryo) are implanted into the intended woman’s uterus. The major drawback is there will be no genetic relation between the intended mother and child.
A donor must be young, healthy, and have normal functioning ovaries. Most importantly the donor must be tested for any genetic disorders. The egg donor program undergoes extensive screening and mentions the background and medical history of the donor. The American Society for Reproductive Medicine recommends that egg donors must be under the age of 34. A donor source could be a family member (genetic link) or a friend. It could be from an egg bank (frozen eggs), or from a fertility clinic.
Older women (over 40) are using the donor egg technique more frequently. In 2010, about 11% of all assisted reproduction techniques used donor eggs with the highest success rate among all.
Following are a few conditions that may demand donor egg IVF.
In a fresh donor egg, immediate fertilization of retrieved eggs and sperm of the intended father or a sperm donor is done. Also, it is a direct transfer of a prepared embryo to the intended mother or egg being frozen for future use. Whereas, frozen donor eggs are retrieved and cryopreserved before fertilization. Later they are thawed and fertilized with the intended father unless the sperm donor is not involved.
In addition, women using fresh embryos (not frozen), have a 43.4% chance of getting pregnant in each cycle.
The treatment cycle starts once the donor and intended mother get their periods. To stimulate egg production the donor is injected with injectable fertility drugs. The intended mother will be given estrogen supplements which will create a suitable lining. Once the egg gets into the maturation step in the donor worm, the intended mother is injected with progesterone which will prepare the uterus to prepare for the embryo. In the next step, the egg retrieval process is done and once done the active role of the donor in the cycle is over. The intended father’s semen sample is being taken. The retrieved donor eggs will be put together with the intended father’s sperm cells. Embryo transfer into the intended mother is done in a fertility clinic. Later the intended mother will take a pregnancy test to see if the cycle was a success.
Low sperm count treatment means that the fluid (semen) you ejaculate or discharge during sexual intercourse contains less than normal sperm. In scientific terms, this condition is known as oligospermia. Low sperm count is considered when the sperm count is less than 15 million sperm per milliliter of semen. Low sperm count decreases the chance that sperm will fertilize the egg and result in pregnancy. However, many men who have low sperm count are still able to father a child.
The important sign of low sperm count is the inability to conceive a child. In some men, some basic problems such as an inherited chromosomal abnormality, a hormonal imbalance, dilated testicular veins or a physiological condition that blocks the passage of sperm may cause signs and symptoms. Symptoms of low sperm count may include:
In many cases, the exact cause of a low sperm count is not known. In some of the cases problems with sperm count and quality are associated with:
In order to protect your fertility, try to avoid known factors that can affect sperm count and quality such as:
Low sperm count treatment includes:
Surgery: Surgery may be helpful for the treatment of a varicocele or for the repair of an obstructed vas deferens. The sperm retrieval technique has been used to retrieve the sperm directly from the testicles or epididymis in cases where no or nil sperm are present.
Treatments for sexual intercourse problems: Medication or counseling can help improve fertility in conditions such as erectile dysfunction or premature ejaculation.
Hormone treatments and medications: Your doctor may recommend hormone replacement therapy or medicines in cases where infertility is due to high or low levels of certain hormones or problems with the way the body utilizes the hormones.
There are several ways you can take at home to boost up your chances of getting your partner pregnant, including:
Increasing the frequency of sex: Having sexual intercourse every day or every alternate day beginning at least four days before ovulation may increase the chance of getting your partner pregnant.
Having sex when fertilization is possible: Women are likely to become pregnant during the ovulation period which occurs in the middle of the menstrual cycle that is between periods. This will confirm that sperm, which can survive for several days, are present when the chances of conception are possible.
Avoiding lubricants: Some of the lubricating agents such as jelly, lotions, and saliva might alter the sperm’s movement and function. Consult with your doctor about sperm-safe lubricants.
Oranges: Vitamin C in the oranges helps to improves sperm motility, count, and morphology.
Leafy vegetables: Vitamin B present in spinach, lettuce, sprouts, and asparagus can help produce strong, healthy sperm.
Dark chocolate: Dark chocolate contains arginine which improves sperm count and quality over time.
Brazil nuts: Brazilian nuts contains Selenium which helps increase sperm count, sperm shape, and sperm motility.
Water: Stay hydrated. It helps create good seminal fluid.
Stress Management During Infertility – After Embryo Transfer, it takes around two weeks for pregnancy test results. This two weeks period is a time of high anxiety, worry, and frustration for women trying to conceive.
Loss of pregnancy is always hard but it becomes more difficult when it has taken so much time and treatment to become pregnant.
She may feel surprised and guilty that she is not joyful about her pregnancy fearing that it may not continue. This could make it hard to relax and enjoy. Talk about the fears and support of the people around her will help.
It depends upon
Though all your emotions are normal it is important to not let these feelings go on for too long and affect your life. Learning to recognise and managing your emotional feeling about infertility is as crucial as looking after yourself physically.
Story of a Brave Donkey – One day a farmer’s donkey slipped and fell down into a deep well. The animal cried mournfully for hours as the farmer was not able to help him.
Ultimately, the farmer thought that since the animal was old it just wasn’t worth it to retrieve the donkey. He decided to cover up the well with mud and bury the donkey.
He also called all his neighbors to come over and help him in filling the well with the mud.
As the donkey understood what was happening he cried unbearably but to everyone’s astonishment, he quieted down and looked relaxed. All were astonished at what they saw.
With each shovel of mud that dropped on the Donkey back, he did something astonishing. The donkey would shake it off and take a step upwards.

As all continued to heap mud on top of the poor animal, he used to shake it off and take a step upwards.
Very soon, all were stunned as the donkey stepped up over the edge of the well and ran off to never come back.
Moral of the story
Life is going to shovel difficulties on you all along.
The lesson is not to get bogged down by them.
We can get out of the deepest well by never giving up

Multiple births are associated with Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) to a large extend.
In the last decade, the cases of women who have given birth to twins or even triplets have increased, which has led infertility specialists to establish a series of guidelines to prevent this, since multiple pregnancies entail more risks than singleton pregnancies.
For couples who have been trying to conceive for a long time, the desire to have a baby is so strong that sometimes they find shelter in the fact that chances of getting pregnant increase if more than a single embryo is transferred. The problem is, most of them do not take into account the risk of multiple births it entails.
Being pregnant with more than one embryo can lead to severe complications for both the health of the mother and the babies. For these reasons, carefully evaluating the pros and cons before making a decision as regards the number of embryos to transfer.
The main cons of multiple pregnancies are due to the risks it conveys for both the mother and the babies, including:
Preterm birth When delivery occurs before 37weeks of pregnancy.
Preeclampsia A type of high blood pressure that occurs during pregnancy. It causes kidney problems, causing the loss of proteins through urine.
Gestational diabetes A type of diabetes that appears for the first time when the woman gets pregnant. It typically appears after the first trimester.
C-section birth A surgical incision is performed on the abdomen and the uterus to deliver the babies.
Postpartum bleeding It is considered if the blood loss exceeds more than 500 ml after a vaginal birth, or over 1,000 ml after a C-section.
Miscarriage or vanishing twin syndrome Although most twin pregnancies develop without problems, the risk of miscarriage is higher than in singleton pregnancies.
Intrauterine growth restriction The fetus is unable to grow as much as it needs due to a deficiency of nutrients and/or oxygen. Usually, it is due to complications in the placenta.
Low birth weight It is diagnosed when the weight is below 2.5 kg.
Perinatal mortality Perinatal death occurs when the fetus dies at week 28 of pregnancy or later, or within the first seven days after being born.
Multiple embryo transfer should be avoided with a focus on a single embryo transfer only.
The “success” of an assisted reproductive treatment does not depend only on achieving pregnancy. We need to be attentive to the fact that the ultimate aim would be delivering a healthy baby and avoiding preterm deliveries.
Egg freezing can be beneficial for women who wish to preserve their fertility for the future, whether this be because they want to focus on their career, have been diagnosed with an illness or are doing so for religious or moral reasons.
Women are born with two ovaries, each containing resting eggs or follicles. Every woman is born with a set amount of eggs. At 20 weeks gestation, a woman has about 6 million eggs, the most eggs she will ever have in her lifetime.
At birth, she will lose approximately half of her eggs, and by the time she reaches puberty, she has only about 200,000 eggs left in her ovaries.
During a menstrual cycle, one egg matures while the remaining eggs that are present that month degenerate.
Ideally, eggs should be frozen when a woman is in her twenties; her prime reproductive years. However, this isn’t always the case, as many women aren’t even thinking about children between these years! Patients who choose to freeze their eggs when they are under 35 tend to have higher success rates than those who are aged 35 and over.
Although sperm and embryos are easy to freeze, the egg is the largest cell within the human body and contains a large amount of water. This means that when it is frozen, ice crystals can form that destroys the cell. Embryologist using some techniques dehydrates the egg and replaces the water with some type of cryoprotectants prior to the freezing process to prevent the ice crystals from forming and damaging the cell.
To harvest the eggs for freezing, the patient undergoes hormone injections as done in any regular IVF cycle.
The only difference between the two procedures is that after egg retrieval they are frozen for some time before they are thawed, fertilized and transferred to the uterus. The egg freezing cycle takes around two weeks to complete. The process includes 10 -15 days of hormone injections to stimulate ovaries and achieving adequate response as to harvest 10-12 eggs from the ovaries.
Once the eggs have matured and follicle have reached 18-20 mm size, they are removed with a needle placed through the vagina under the guidance of an ultrasound. This procedure is not painful and is done under IV sedation. Eggs are quickly frozen and kept at -196 degree temperature.
When the patient is ready to start her family the eggs are thawed and injected with a single sperm to achieve fertilization. Resulting embryos are then transferred to the uterus as done routinely.
Scientific evidence suggests that long-term freezing of eggs does not result in any decrease in quality.
It is recommended that ten eggs should be frozen for each pregnancy attempt.
There is a variation across these figures depending on many factors, including competence of the embryologist and age of the patient. Younger women can be expected to produce more than ten eggs. Younger eggs would have higher chances of implantation than eggs of elderly women.
The age of the woman at the stage of thawing and implantation has an insignificant impact upon the overall outcome.
Depending on the age of the egg at freezing, each cycle would have a 15-30% chance of leading to a live birth.
It is recommended that 10 eggs be stored for each pregnancy attempt. 2-3 cycles may be done and adequate no of eggs be frozen for latter use.
The chance of future IVF pregnancy with her frozen eggs in women older than 38 at the time of freezing is likely to be lower than that seen for younger women.
To date, approximately 5,000 babies have been born from frozen eggs. The largest published study of over 900 babies from frozen eggs showed no increased rate of birth defects when compared to the general population. Additionally, results from one study showed no increased rates of chromosomal defects between embryos derived from frozen eggs compared to embryos derived from fresh eggs.
The costs for egg freezing are identical to those of routine IVF. In general, it costs 1.8 lac INR to undergo an egg freezing cycle. This estimate includes all testing, monitoring, medications and egg freezing.
The egg-freezing fee includes the storage fee up to the end of the calendar year. There will be afurther annual storage fee beginning January 1st of the next full calendar year.
Are you under stress and confused?
Every month during ovulation, an egg is produced by one of the ovaries. The mature egg is carried from the ovary to the uterus through a thin oviduct or fallopian tube. When a blockage prevents the egg from traveling down the tube then the woman is having blocked fallopian tube, also known as tubal factor infertility or hydrosalpinx. This can occur on one or both sides.
Hydrosalpinx commonly results from a prolonged untreated infection of the fallopian tubes. Common causes are:
Blocked tubes are diagnosed by following tests:
Hysterosalpingography is a procedure used to diagnose the shape of the uterus and the shape and patency of the fallopian tubes. This test uses X-rays along with a dye to look into the uterus and the fallopian tubes. The whole process takes around 5-10 minutes and patient is allowed to go home the same day.
In the presence of hydrosalpinx the pregnancy rate and implantation rate is reduced by 50% and the risk of spontaneous abortions is doubled. Many studies have shown patients with hydrosalpinx have lower pregnancy rates when compared with patients with tubal infertility without hydrosalpinx.
Both bilateral hydrosalpinx and large size hydrosalpinx visible on ultrasound are associated with a significant reduction in pregnancy rate as compared to unilateral hydrosalpinx and hydrosalpinx not visible on ultrasound.
The risk of ectopic pregnancy and miscarriage rate is not affected by presence of hydrosalpinx. The negative effect of hydrosalpinx was also seen in patients who underwent frozen embryo transfer, suggesting that it is the failure of embryo implantation and not oocyte quality that decreases the reproductive outcome. The tubal fluid is believed to be the main culprit behind the negative effect of hydrosalpinx on the pregnancy rate. That’s all about blocked tubes diagnosis.
Fertility preservation is an effort of preserving eggs, embryos, and sperms of individuals who have been diagnosed with cancer or are preparing to undergo treatment, so that they can have children in the future. This method allows these individuals to remain potentially capable of having children once the treatment is complete.
Ovarian follicles are vulnerable to agents that lead to DNA damage, including ionizing radiation and chemotherapy, at any age. Such anticancer treatments lead to a reduction in the ovarian follicle reserve in a dose-dependent manner, and can eventually cause amenorrhea and premature ovarian failure.
Alternatively, there could be the occurrence of partial ovarian injury, in which the reduction in primordial follicle stockpiles is manifested by infertility along with a shortened reproductive lifespan despite the resumption of menses following the treatment of cancer. In such instances, the post-cancer treatment markers of ovarian reserve (Antral follicle count, FSH, Anti- Mullerian Hormone [AMH], inhibin B) can often resemble the levels similar to those seen in premenopausal women.
Women who are young or wishing to postpone maternity then embryo and oocyte cryopreservation are first-line Fertility Preservation methods in post-pubertal women.
Ovarian tissue auto-transplantation in post-pubertal women is capable of restoring fertility with over 100 live births currently reported with a corresponding pregnancy rate of 23 to 37%. The recently reported successes of live births from transplants, both in orthotopic and heterotopic locations, as well as the emerging methods of in vitro maturation (IVM), in vitro culture of primordial follicles, and the feasibility of In vitro activation (IVA) propose new fertility options for many women and girls.
Vitrification has also demonstrated successful live births and may be a more cost-effective method to freezing with less tissue injury.
Ovarian tissue freezing is the only option to preserve fertility in young cancer patients who have recently been exposed or are to be exposed to chemotherapy treatments. The technique mainly avoids injury to the primordial follicles, which are not subject to the deleterious effects of chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
The technique of ovarian tissue freezing involves following steps:
If what to do is in your mind. You don’t know what to do. Please approach us.
Sperm donation is the process by which a man, known as a sperm donor donates his semen to a recipient via ART semen bank with the intention that it be used to achieve a pregnancy and produce a baby in a woman who is not the man’s sexual partner. Sperm donation is a means of third party reproduction.
The assisted reproductive technology clinics and assisted reproductive technology banks shall ensure that information about the couple, donor is kept confidential and that information about assisted reproductive technology treatment shall not be disclosed to anyone other than a central database to be maintained by the National Registry except in a medical emergency at the request of the couple to whom the information relates, or by an order of a court of competent jurisdiction.
The assisted reproductive technology clinics shall obtain donor gametes from the assisted reproductive technology banks that have ensured that the donor has been medically tested for such diseases as may be prescribed.
The screening of gamete donors, the collection, screening and storage of semen;shall be done by an assisted reproductive technology bank registered as an independent entity under the provisions of this Act.
The assisted reproductive technology banks shall obtain semen from males between twenty-one years of age and forty-five years of age, both inclusive and examine the donors for such diseases, as may be prescribed.
Ovarian reserve is a theoretical concept. As a practical matter, it refers to the ease at which an individual’s ovaries can be successfully stimulated with fertility drugs. It indicates quantity and quality of oocytes in women of reproductive age group.
The single most consistent variable affecting ovarian reserve is the woman’s age. This is because a woman is born with all the eggs she will ever have.
In most women majority of the eggs are genetically normal or balanced. However, there will be some that are genetically abnormal or unbalanced.
It appears that the best eggs are ovulated first. The older a woman is, the fewer genetically balanced eggs she has left to respond to fertility drugs. This age relationship holds true even in the fertile population.
It indicates a reduction in quantity and quality of oocytes in women of reproductive age group.
An AFC (antral follicular count) of 4 put together in both the ovaries and serum AMH value of less than or equal to 0.28ng/ml is considered to be indicative of decreased ovarian reserve.
There is a risk of Low pregnancy rates irrespective of age and a high pregnancy loss.
Any of the two criteria out of three should be present to diagnose poor ovarian reserve:
Reproductive aging is a continuous process from before birth till menopause. Throughout reproductive life there is a progressive and irreversible loss of the eggs which apart from natural age related decline, certain factors may further deplete the ovarian reserve like endometrioma, certain pelvic infections, ovarian surgery, chemotherapy ,radiotherapy, etc . So the ovarian reserve reduces early and patient may have early menopause also.
The management of poor ovarian reserve patients is challenging, pregnancy rates are very low with simple forms of treatment, and IVF in such women offers the highest probability of pregnancy and antagonist protocol is most preferred one. When repeated attempts at treatment become unsuccessful, the only options that remain are recourse to oocyte donation or adoption.
Low sperm count is the term used to define the condition when men have fewer than 15 million sperm per milliliter of semen when compared with normal. It is also called oligospermia.
Having a low sperm count reduces the chances of pregnancy. However, many males that have a low sperm count but are still in a position to father a baby as sperm count varies in men.
No sperm count is the term used to define the condition when men have complete absence of spermatozoa in the ejaculate even though they may be producing sperm. It is also called azoospermia and is associated with infertility. In humans, azoospermia affects nearly 1% of the male population and may be seen in up to 20% of male infertility situations.
When sperm cannot move through a man’s genital tract because of any obstruction, or if there is a mechanical problem with them getting to where they need to be, sperm can be retrieved through surgical sperm extraction methods such as:
The most of the semen ejaculate volume is contributed by secretions from seminal vesicles and prostrate gland. If there is low semen volume (≤1.5 ml) one should first rule out the possibility of spillage of semen sample during collection and then confirm the results by repeat semen analysis.
After confirming the low semen volume then one should suspect the other physiological reasons for some kind of abnormality or obstruction as highlighted below:
When low percentage of live, and high percentage of immotile, spermatozoa are present in an ejaculate then it is called necrozoospermia.
Sperm vitality is the test, which will reveal the proportion of spermatozoa that are “alive” and the proportion of the spermatozoa that are “dead”. The percentage of live spermatozoa is assessed by identifying sperms with an intact cell membrane, from dye exclusion or by hypotonic swelling sperm function test.
If what to do is in your mind. You don’t know what to do. Please approach us.
Recurrent miscarriages affects 1-2 percent of reproductive age women. However in India the prevalence is 7.4%. Researchers have been intrigued by the complexity of the factors causing it and treatment that may help to prevent or manage it. It is important for clinicians to be updated with the evolving investigations and evidence based treatment options to mange couples with recurrent miscarriages.
ESHRE/ RCOG/ASRM/MOHFW: Depending upon the gestation of viability and epidemiological data each society has different definition of Miscarriage and RM (Recurrent Miscarriages)
GDG of ESHRE Defines: A pregnancy loss is defined as the spontaneous demise of a pregnancy before the fetus reaches viability. The term therefore includes all pregnancy losses from the time of conception until 24 weeks of gestation.
The term Recurrent Pregnancy Loss for two or more pregnancy loss and to reserve ‘recurrent miscarriages’ to describe cases where all pregnancy losses have been confirmed as intra-uterine miscarriages.
RCOG: Uses 24 weeks as the cut off for viability and defines recurrent miscarriages as the loss of three or more consecutive pregnancies (< 24 weeks).
MOHFW: Miscarriage is defined as a spontaneous loss of pregnancy before 20 weeks of gestation.
Recurrent Miscarriages: Women with three or more first trimester and one or more second trimester miscarriage. Early evaluation is considered if fetal cardiac activity was present, women >35 years with two or more abortions and the couple has had difficulty in conceiving. Women with two or more losses with one or more live issues should be excluded.
ASRM: Recurrent pregnancy loss is two or more failed pregnancy where pregnancy means a clinical pregnancy documented by ultrasound or histopathology.
Working definition warranting investigation & work up and management accordingly.
Miscarriage: Any pregnancy loss from conception till the fetus reaches viability (<24 weeks) Couples with more than two miscarriage should be evaluated consecutively or non consecutively. This would include clinical and biochemical pregnancies but excludes ectopic, molar pregnancies and implantation failure in ART.
In absence of adequate data on the effect of a non consecutive pregnancy loss on the subsequent pregnancy, they should not be clearly excluded from evaluation. Although no distinction in the definition criteria for first or second trimester loss in made but any obvious factor leading to pregnancy loss should not be ignored.
Terminology like Primary RPL (multiple losses in a woman with no previous viable infants) secondary RPL (multiple losses in a woman who has already had a pregnancy beyond 20 gestational weeks) and Tertiary RPL (multiple pregnancy losses between normal pregnancies) are clinically irrelevant for investigating a case of RPL.
Ideally there should be dedicated RM Clinic which in-depth investigates the couples with recurrent miscarriages. Clinicians and clinics should take the psychosocial needs of couples faced with RM into account when offering and organizing care for these couples. Investigations need not necessarily lead to treatment options and this should be explained to the couple from the beginning. The prognosis and recurrence prediction charts should be used to counsel the couples and overall the chances of successful live birth after RM are satisfactory.
What are the Risk Factors for having RM: Recurrent miscarriages are associated with following risk factors. Some of them are modifiable and adoption of health changing behavior can lead to definitive reduced risk of another miscarriage. While for other non modifiable factors various treatment modalities have been tried but only a few can be recommended to be used based on the scientific literature published.
BMI: Maternal obesity has a strong association with repeated miscarriages but the direct effect of weight loss in achieving live birth is not studied. But weight loss definitely decreases time to conceive and risk of miscarriages and other medical obstetric complications like pregnancy induced hypertension, diabetes and metabolic syndrome in general. Also on the other hand a BMI of less than 18.5 is found to be associated with sporadic first trimester losses. Achieving optimal BMI should be a treatment goal in management.
Exercise in pre pregnancy and during pregnancy is found to have no negative effect on the pregnancy outcome rather it benefits by improving tissue oxygenation and helping achieve normal BMI.
Smoking: Smoking has not been conclusively found to be a risk factor for RM but based on its definitive association with poor obstetric outcomes, cessation of smoking should be advised in couples with RPL even in absence of data supporting smoking cessation and chance of live birth.
Caffeine: A study on small population found a linear correlation between the amount of caffeine intake in pre-pregnancy and early pregnancy period and pregnancy loss, maximum being with >300mg/day of caffeine consumption compared to mild consumption > 150 mg/day. However the chances of live birth on caffeine intake reduction is not studied.
Alcohol: Alcohol consumption is associated with pregnancy loss and fetal alcohol syndrome. Seeing the negative effects of alcohol even in absence of direct causal relation it is advised to limit or curtail alcohol consumption in the pre-conceptional period.
Stress: Stress is associated with RPL but direct causative relation has not been established due to non-uniformity in type of scales used and poor study designs.
Endometritis: Very small studies have found the presence of endometritis in women with RPL and improving with antibiotic treatment, however these studies are inadequately designed to form basis for screening for endometritis.
Age: Advanced female age is associated with sub fertility, genetic anomalies, obstetric complications, still births etc. The risk of another miscarriage in woman with RPL has been found to double after the age of 35 years. Woman should be told that the risk of RPL is lowest between 20-35 years and rises rapidly after 40 years.
Occupational and environmental exposure: Based on only a few small studies, exposure to occupational and environmental factors (heavy metals, pesticide, lack of micronutrients) seems to be associated with an increased risk of pregnancy loss in women with RPL.
Genetic: Majority of early pregnancy losses (50%-60%) are due to chromosomal abnormalities resulting as a de novo process or are parental in origin. Most common parental abnormalities leading to miscarriages are translocations (2-4%) which can be Reciprocal (60%) equal exchange of genetic material between two chromosomes or Robertsonian (40%) where long arm of two acrocentric chromosomes join together. Carrier parents are asymptomatic. These can be picked up by karyotyping of parents. The karyotype of products of conception can be normal or have a balanced or an unbalanced translocation. Pregnancies with unbalanced translocations usually end in miscarriage, still births and rarely anomalous babies.
Immunological: The association between HLA (Human Leucocyte antigen) polymorphism and RM is inconsistent. Of the various types a weak association is found between HLA-G alleles with RM. Investigation of HLA in women with RM is not recommended except class II HLA in women with secondary RPL after the birth of a boy.
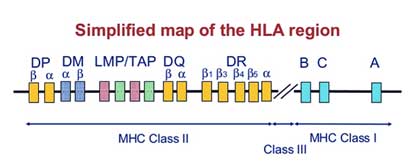
There should be individual evaluation of the investigations appropriate to each woman or couple, based on age, fertility/sub-fertility, pregnancy history, family history, previous investigations and/or treatments. In addition, care should be tailored to the psychological needs of the couples.
Products of Conception: Aneuploidy is the most common cause of early pregnancy losses and the risk increases with age of the woman. Aneuploidies occur in comparable frequencies in both women with sporadic and recurrent pregnancy loss. Although not mandatorily recommended but genetic analysis of the products of conception help in explanatory purpose and may help to determine whether further investigations or treatments are required. For Genetic analysis of POCs array CGH is recommended.
Parental Karyotype: The test should be advised only after individual risk assessment. Parental karyotyping is advised based on genetic history (history of previous child with congenital abnormalities, offspring with unbalanced chromosome abnormalities in the family, or detection of a translocation in the pregnancy tissue). In couples with female age above 39, less than three pregnancy losses and a negative family history, the chance of being a carrier of a translocation is very low.9 The information from parental karyotype however helps couples in deciding continuing to try to conceive, stop trying, or choose invasive tests like prenatal diagnosis or preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) (for instance PGT-SR in case of a balanced translocation)
Acquired : Antiphospholipid antibody syndrome is associated with RM by action of anti PL in complement activation and vascular thrombosis. The Miyakis criteria (2006), an update of the Sapporo classification of 1999, is used to diagnose antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. This requires presence of one clinical criteria and elevated levels of aPL antibodies. (box) Screening for antiphospholipid antibodies, Lupus anticoagulant, Anti cardiolipin antibody and aβ2GlycoProtein I should be considered after two pregnancy losses at least 6 weeks after a miscarriage.
Hereditary: There is no, or a weak association at best, between RPL and hereditary thrombophilia. It is hence not recommended to screen for hereditary thrombophilia in women experiencing RPL however in presence of additional risk factors for hereditary thrombophilia like family members with hereditary thrombophilia, or previous VTE, screening can be considered.
Presence of uterine malformations is more common in woman with RM. The association is strong for congenital than acquired ones and treating them has improve live birth rates in some studies. All women with RM should be screened for malformations. The preferred technique to evaluate the uterus is transvaginal3D ultrasound (3D US), which has a high sensitivity and specificity compared to a 2D US. Sonohysterography (SHG) is more accurate than hysterosalpingography (HSG) in diagnosing uterine malformations more so when tubal patency has to be investigated. MRI is not the first line investigation.
Congenital Abnormalities: Potentially relevant congenital Müllerian tract malformations include septate uterus, bicorporeal uterus with normal cervix (AFSbicornuate uterus), bicorporeal uterus with double cervix (AFSdidelphic uterus) and hemi-uterus (AFSunicornuate uterus).
Acquired Abnormalities: Acquired uterine malformations (submucousal myomas, endometrial polyps and uterine adhesions) have been found prevalent in women that suffered pregnancy loss, but the clinical relevance is unclear. 3 D USG is a better screening tool. When suspected, a hysteroscopy has to be performed. It is the gold standard.
Cervical Incompetence: Women with a history of second-trimester pregnancy losses and suspected cervical weakness should be offered serial cervical sonographic surveillance.
Thyroid &antoTPO, Diabetes Mellitus, Androgens &LH: Thyroid screening (thyroid-stimulating hormone [TSH] and thyroid peroxidase [TPO]-antibodies) is recommended in women with RPL. Abnormal thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) and thyroid peroxidase [TPO]-antibody levels should be followed up by thyroxine (T4) testing in women with RPL. Assessment of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), fasting insulin and fasting glucose, baseline androgen levels and LH is not recommended in women with RPL to improve next pregnancy prognosis. However prolactin testing should be undertaken in symptomatic women (Oligo/amenorrhoea). Routine testing for luteal phase insufficiency in neither feasible nor necessary in women wit RM.
HLA determination in women with RPL is not recommended in clinical practice.
List of tests & Recommendations (Table)
| Test | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| anti-HY antibodies | Not recommended |
| Cytokine testing | Not recommended |
| Cytokine polymorphisms | Not recommended |
| Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) testing | Could be considered for explanatory purpose |
| natural killer (NK) cell testing | Insufficient evidence to recommend |
| anti-HLA antibodies | Not recommended |
The role of male factor in RM is being investigated owing to the fact that female causes explain only about 50-60% cases of RM.
Assessment of spam DNA fragmentation can be considered for explanatory purposes not therapeutic purpose based on indirect evidence.
Endometrial aspiration to screen for endometritis is not recommended due to lack of evidence and the diversity of nature of infectious agent being studied and treated in various studies.
Introduction: The treatment in RM could be specific in 50-60% cases where aetiology is identified by the extensive work up the couple undergoes or it is empirical as used in the remaining 40-50% cases of unexplained RM. In either scenario the psychological needs and expectation of the couple from treatment should be well dealt.
Prognosis: Couples are keen to not only know the cause but also the chances of recurrence of such an event in case specific manner. Few prognostic tools (Lund and Brigham) were evaluated, that is female age, number of preceding losses can guide about the prognosis.
Treatment options specially the empirical ones or the ones with insufficient evidence should be offered based on reasonable pathophysiological hypothesis and after adequate information to the couple.
Role of PGT-M and PGT-SR: Preimplantation genetic testing for monogenic/single gene defects (PGT-M) or chromosomal structural rearrangements (PGT-SR), previously PGD, is an established method to preconceptionally select the genetic defect free embryo for transfer in couples with a high risk of transmitting genetic disorders.Structural chromosomal defects are common in RM population and PGT is useful in couples who are carrier of translation to prevent miscarriage although this is backed by limited evidence and lack of RCT’s
All couples with abnormal genetic results from pregnancy tissue testing or parental karyotypes should be offered genetic counseling to discuss likely prognosis and further diagnostic options. In addition, couples should be informed that PGT-SR could reduce the miscarriage rate, but will not improve live birth rate or time to pregnancy.
Role of PGT-A in unexplained RPL: Preimplantation genetic testing for aneuploidy (PGT-A) (previously preimplantation genetic screening [PGS] or preimplantation diagnosis of aneuploidy [PGD-A]), where an IVF cycle creates embryos which are biopsied and screened for chromosomal anomalies prior to implantation, has been proposed as a potential treatment for RM. However systematic reviews on PGS (PGT-A) for unexplained RM concluded that there is no improvement in live birth rate and hence not cost effective.15
Role of Anticoagulants: Aspirin & LMWH
APS: Women who fall under the diagnosis of APS based on the criteria are advised to take low dose aspirin (75-100mg/day) before conception and prophylactic dose of LMWH or unfractionated heparin from the day of pregnancy test positive. For women with hereditary thrombophilia and a history of RPL, antithrombotic prophylaxis is not recommended unless in the context of research, or for venous thromboembolism (VTE) prevention.
No role of steroids or IvIG for this indication
Diagnosis of immunological cause is a dilemma and in absence of clear evidence no specific treatment can be recommended.
| Procedure with RM | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Hysteroscopic septum resection | Needs evaluation for RM (ESHRE). But GPP should be done |
| Metroplasty for bicorporeal uterus with normal cervix | Not recommended |
| Uterine reconstruction for hemiuterus | Not recommended |
| Metroplasty in women with bicorporeal uterus and double cervix | Insufficient evidence |
| Hysteroscopic removal of submucosal fibroids or endometrial polyps in women with RPL | Insufficient evidence but GPP should be done |
| Surgical removal of intramural fibroids | Not recommended |
| Im fibroid distorting the cavity | Insufficient evidence GPP: decision should be individualized |
| Surgical removal of intrauterine adhesions | Insufficient evidence |
| Cervical cerclage : singleton pregnancy and a history of recurrent second-trimester pregnancy loss attributable to cervical weakness | Recommended |
| Lymphocyte immunization therapy | Should not be used, may have serious adverse effects |
| Intravenous immunoglobulin (IvIg) | Not recommended |
| Glucocorticoids | Not recommended |
| Heparin or low dose aspirin | Not recommended |
| Folic Acid | Not recommended for RM prevention, given routinely to prevent NTD |
| Vaginal progesterone | Insufficient evidence |
| granulocyte- colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) | Insufficient evidence |
| Intralipid therapy | Insufficient evidence |
| Endometrial Scratching | Not recommended |
One of the commonest endocrine disorders, affecting approximately 5-10% of women in young and reproductive age group.
The syndrome is present throughout a woman’s lifespan from puberty across post-menopause and affects women of all ethnic groups.
Genetic, environmental factors, along with obesity, hormonal issues, ovarian and metabolic dysfunctions, are the main causes of PCOS.
Presence of excessive acne, scalp hair loss, and or hirsutism (terminal hair in a male-pattern distribution) or biochemically, by elevated serum levels of LH and testosterone.
Ovary having 12 or more follicles of 2 to 9 mm in diameter or and having a volume of greater than 10 ML.
Infrequent menstrual periods (fewer than six to eight periods per year).
Insulin resistance is a state in which the body’s cells do not respond to the metabolic effects of insulin hormone. When the body does not react to insulin, the level of glucose in the blood rise. This leads to more insulin to be secreted as the body tries to move excess glucose into cells. Such Impending Insulin resistance can lead to diabetes mellitus and is also associated with acanthosisnigricans a common skin disorder.
For the overweight women, weight loss may help in regularizing the menstrual periods. A moderate loss of 4-5 kg can be helpful in making menstrual periods more regular. Weight loss is also been found to improve raised cholesterol and insulin levels and thus relieving common symptoms as excessive hair growth and acne.
Achieving successful ovulatory cycles are the first step toward attaining a pregnancy. For overweight women and those with raised BMI, weight loss often achieves this goal. Medications may also be used to for successful ovulation.
Insulin-sensitizing drugs may be used in the treatment of PCOS. Such drugs help the body in responding towards raised insulin levels. In PCOS women such drugs can help decrease androgen levels thus improving ovulation. Restoring the ovulation would help in making the menstrual periods regular and more predictable.
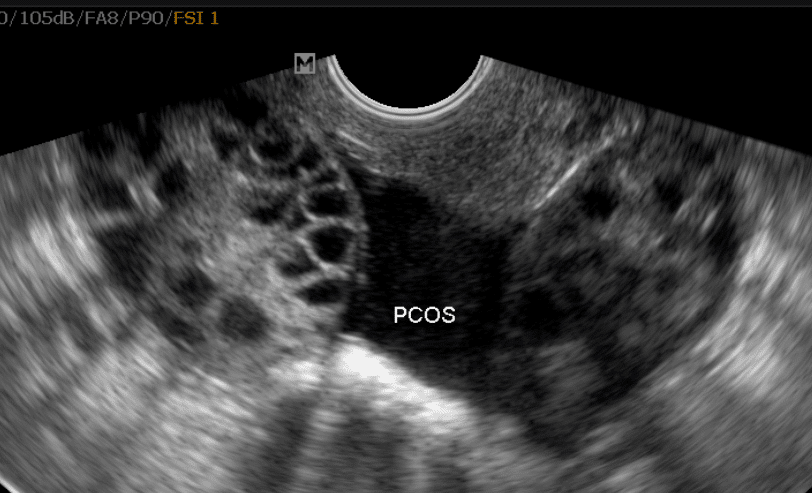
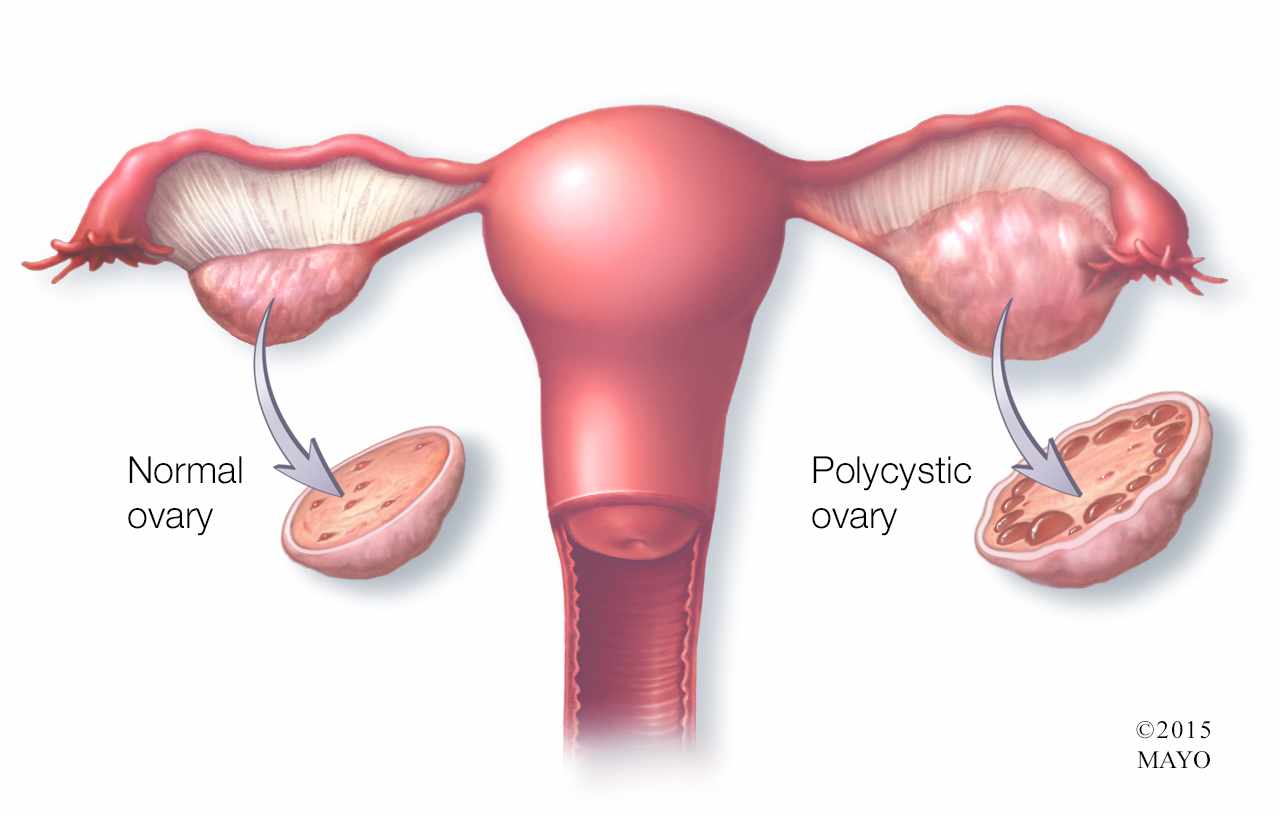
Has your doctor advised you IVF – ET?
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a process of fertilization where an egg is combined with sperm outside the body, in vitro (“in glass”). The process involves monitoring and stimulating a woman’s ovulatory process, extracting ova, retrieving a sperm sample and then manually combining an egg and sperm in a laboratory dish. After fertilization, the zygote undergoes embryo culture for 2–5 days. It is then implanted in the same or surrogate mother’s uterus, with the intention of establishing a successful pregnancy
The IVF procedure could be somewhat different for different patients, depending upon the type of reproductive technique being used. But the basic steps involved in the procedure are:
IVF success depends on a variety of factors that could be maternal age, factors causing infertility, reproductive history, whether donor gametes being used or not, lifestyle factors, embryo status, etc.
Generally, IVF treatment has excellent success rates i.e in younger women (age less than 35 years) the percentage of live births per IVF cycle is about 40-45% while in older women (age more than 40 years) the percentage of live births per IVF cycle is 10-12%.
IVF is not a single treatment but a series of procedure and for a woman, the IVF process actually starts weeks earlier. One cycle of IVF cycle takes between four to six weeks to complete from consultation to embryo transfer, but depending on the specific circumstances of each the protocol is similar for every patient.
Age is probably the most important factor influencing the outcome of an IVF cycle and its restrictions for IVF vary from clinic to clinic. In general, women older than age 40 have a markedly lower chance for a live birth compared with women younger than 40 years old.
No. The process of IVF in and of itself does not lead to high risks of multiple pregnancies. But in order to increase the chances of pregnancy, clinicians transfer two to three embryos in younger and older women respectively, which may end up in getting twins or triplets. Also, the probability of conceiving with multiples increases with the number of embryos transferred during IVF. That’s all about (Has your doctor advised you IVF – ET).
On an average, cost of IVF treatment ranges from 1.5 lakhs to 2 lakhs with additional cost for ICSI and freezing (this includes the drug charges.
IUI stands for “Intra Uterine Insemination”, a fairly new form of assisted fertilization. IUI involves the placing of freshly prepared sperm (from your partner or from a donor depending on the case) high in the uterine cavity at a selected time in your menstrual cycle. Conception is then allowed to occur naturally. These procedures are carried out on an outpatient basis and you need not be admitted to hospital.
Ideally, couples that have unexplained sub fertility and in woman where there is no evidence of damaged fallopian tubes. It may also help those who have minimal endometriosis or some male factor.
Intrauterine insemination is done very often in following conditions –
There are three components of IUI which help in improving the results.
Following precautions should be taken for sperm collection:
The patient is made to lie down in Lithotomy position in a comfortable room on a standard gynae examination table with a U cut after evacuating the bladder. The patient is asked to read the identifying data on the test tube containing the sample. Specimen is aspirated in the IUI Cannula and 1 ml syringe without disturbing the pellet.
The semen sample is collected by ejaculation into a sterile wide mouth container collection jar meant for use in ART procedures only.An appropriate semen collection room should be used for this.
Semen should be collected,analyzed and prepared within 60 min of ejaculation.
We perform the IUI as soon as possible after washing is completed for optimal results.
Ideally an IUI should be performed approximately 36 hours after the ovulation trigger or after confirming the ovulation on ultrasound.
If two IUIs are scheduled, they are usually spaced at least 12 hours apart between 24 and 48 hours after the hCG.
Some units plan the timing of IUI on a natural LH surge. In that case, a single IUI at 36 hours is the norm.
We have to remember that the egg is viable only for a maximum of 24 hours after it is released.
Natural cycle IUI, in which no fertility drugs are used, tend to have lower success rates amounting to about 6-8 % in some cases. Overall a success rate of 12% to 18 % is expected with an IUI procedure.
Maximum women perceive IUI to be fairly painless procedure baring slight pain as felt during an IUI procedure.
Sperm washing must be done before IUI is performed. The process can take 20 min- 40 minutes with different sperm wash techniques. Insemination should occur shortly after the sperm has been prepared.
Psychological Complications: IUI may result in psychological complications such as sexual dysfunction, fear of congenital malformations, mix-up of samples etc. Careful counseling and precautions can avoid these problems.
Mostly ICSI is indicated for the cases with:
ICSI is a procedure which effectively eliminates male infertility by introducing sperm cell directly into an egg, hence increases chances for fertilization for male factor.
Right choice if you have male factor infertility/ repeated IVF failure.
ICSI conceived children are not at a higher absolute risk of any disease or illness.
Intracytoplasmic morphologically selected sperm injection (IMSI) is a variation of ICSI that uses a high power microscope to select sperm. This allows embryologists to look at the sperm in greater detail at 6600X magnification.
DNA damage occurs at the post-testicular level, hence testicular sperm may have a better DNA integrity than ejaculated sperm.
Fertility preservation is an effort of preserving eggs, embryos, and sperms of individuals who have been diagnosed with cancer or are preparing to undergo treatment, so that they can have children in the future. This method allows these individuals to remain potentially capable of having children once the treatment is complete.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapies for cancer can affect reproductive health and potential of adolescents and young adults.
The protocols that impede ovarian and testicular function are radiotherapy to the pelvic area and lower abdomen and types of chemotherapy and drugs administered.
Chemotherapies with high risk include procarbazine and alkylating drugs such as cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, busulfan, melphalan and chlorambucil.
Some Drugs with medium risk to the fertility potential are doxorubicin and platinum analogs such as cisplatin and carboplatin.
On the other hand few drugs have low risk of gonadotoxicity post treatment. These are plant derivatives such as vincristine and vinblastine. Antibiotics such as bleomycin and dactinomycin and antimetabolites as methotrexate and 5-fluoruracil also have low toxicity potential.
These drugs specifically attack the dividing cells in the body, including healthy cells having reproductive potential such as spermatozoa and ovarian egg. Depending on the dose and duration of administration, these cures can have varying effects on reproductive health and potential.
Women have option of oocyte freezing, embryo freezing, ovarian cortex freezing or ovarian transposition.
The men can undergo semen freezing or testicular tissue freezing. The other options can be modification of the chemotherapy drugs and dosages and timely treatment.
Always remember that Pre chemo- radiation therapy fertility management is a better option.
Early action is the treatment. Children are young and don’t understand the ethical issues involved in the management of such cases.
If the child is pre pubertal age, options include testicular and ovarian cortex freezing.
In the post-pubertal age group – oocyte or sperm cryopreservation may be done. Legal consent has to be taken before any intervention.
Efforts to preserve the fertility of a pre pubertal are to be weighed carefully in children, as these techniques are generally experimental.
If you want to preserve your fertility before cancer treatment or immediately thereafter, have a dialogue with your family physician, oncologist or a reproductive specialist.
Your treating team will consider the type of cancer you have depending upon the biopsy report. The treatment plan and the amount of time you have before chemo-radiation is initiated helps to determine the best approach for your fertility preservation.
Obtaining information about fertility preservation methods before you start cancer treatment can help you take a well informed decision.
A hydrosalpinx may be seen incidentally at CT as a fluid-attenuation tubular adnexal structure, separate from the ovary. A simple hydrosalpinx is not accompanied by pelvic inflammation. The tubal wall may enhance following contrast.
MR imaging is the modality of choice for the characterization and localization of adnexal masses that are inadequately evaluated with ultrasound. MR imaging also may be useful for determining the cause of a hydrosalpinx or its associated adnexal process by characterizing the nature of the contents of the dilated tube
Ultrasound In Adenomyosis
It is an excellent tool for management of adenomyosis. The main criteria for the definition of adenomyosis on MRI are
Planned Procedure to start with one of the best IVF treatment Centres in Delhi, NCR, Gurugram with our IVF Specialist Dr. Pankaj Talwar.

